Single Sign On
advertisement
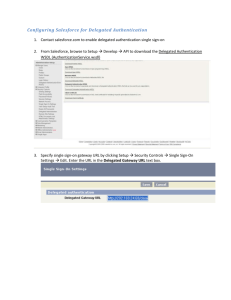
SINGLE SIGN-ON Definition - SSO Single sign-on (SSO) is a session/user authentication process that permits a user to enter one name and password in order to access multiple applications. The process authenticates the user for all the applications they have been given rights to and eliminates further prompts when they switch applications during a particular session. Common Examples Common single sign-on configuration Kerberos based systems Smart card based system One-time password Integrated windows authentication Social Aspect Following are social aspect of SSO Reduces phishing success, because users are not trained to enter password everywhere without thinking. Reducing password fatigue from different user name and password combinations Reducing time spent re-entering passwords for the same identity Reducing IT costs due to lower number of IT helpdesk calls about passwords and infrastructure cost Security on all levels of entry/exit/access to systems without the inconvenience of re-prompting users Centralized reporting for compliance adherence. Potential Issues As single sign-on provides access to many resources once the user is initially authenticated, it increases the negative impact in case the credentials are available to other persons and misused. Therefore, single sign-on requires an secure authentication mechanism. List of Products Following products are available for single sign-on implementation Microsoft Forefront Identity Manager IBM – Tivoli security access manager Kerberos – Computer network authentication protocol HP Ice Wall SSO – Web and Federated single sign-on Custom in-house built solution Cost Analysis In-House Solution = $100,000 (no additional support cost) IBM = $590,000 plus annual support costs Microsoft = $231,000 plus annual support Based on 5,000 user estimate. Software only costs, no additional hardware figured into this estimate Business Aspect Helps business to bring multiple system into one umbrella. It allows business to move multiple applications towards the portal strategy. Portal lets user to authentication once and then based on authorization system allows them to navigate to other applications. Summary Decision to go with Single Sign-On Security, Safety, User convenience, and reduced IT load Customized Proprietary Solution Cost, adaptability, flexibility This solution summary is geared towards a large company with 5,000+ users. A small 100 user shop would have different priorities and needs in the final choice. They might be more likely to go with an off-the-shelf solution for easier support with a smaller IT staff. Questions? Thank you!