Concepts of management leadership-motivation and organizational
advertisement

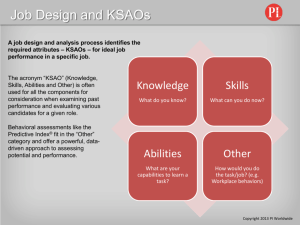
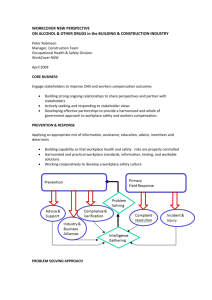
Concepts of management leadership-motivation and organizational culture B.V.L.Narayana Definitions • Motivation – To be moved to do something – Vary in • Degree or intensity • Logic behind motivation –orientation—”why” • Intrinsic –inherently interesting or enjoyable – Related to needs of competence, autonomy, relatedness—based on free choice, enjoyment – Internal perceived locus of causality • Extrinsic-leads to a separable outcome – Instrumental value-non autonomous; internalization and integration –leads to intrinsic control Motivation • Extrinsic motivation – External perceived causality • Self determination theory – SDT postulates that autonomous and controlled motivations differ in terms of both their underlying regulatory processes and their accompanying experiences, and it further suggests that behaviors can be characterized in terms of the degree to which they are autonomous versus controlled. Source :Deci and Ryan 2000 Leadership • Leadership is – Ability to influence others – Influence is ability to convince others to do what you want – Consists of • Thinking abilities • People abilities • Task abilities ROLE OF LEADERSHIP • Leadership – – – – Process of social influence Which enlists the aid of people To achieve something(extraordinary) Or • Creating a way for people to contribute • Contribute in form of – Ideas, effort, resources, • Achieve – Common goals ROLE OF LEADERSHIP Organizational culture • Schein (1990) defines culture as, "…a) a pattern of basic assumptions, b) invented, discovered, or developed by a given group, c) as it learns to cope with its problems of external adaptation and internal integration, d) that has worked well enough to be considered valid and, therefore e) is to be taught to new members as the f) correct way to perceive, think, and feel in relation to those problems • The set of shared attitudes, values, goals, and practices that characterizes an institution, organization or group (Wikipedia) COMPETING VALUES FRAME WORK • Developed by QUINN and CAMERON • Organizational culture assessment instrument • Based on polarities – Internal versus external focus – Stability versus flexibility • Four types of culture Types of organizational cultures • Clan Culture - internal focus and flexible A friendly workplace where leaders act like father figures.—all A’s • Adhocracy Culture - external focus and flexible A dynamic workplace with leaders that stimulate innovation—all B’s • Market Culture - external focus and controlled A competitive workplace with leaders like hard drivers –all C’s • Hierarchy Culture - internal focus and controlled A structured and formalized workplace where leaders act like coordinators— all D’s DIMENSIONS OF LEARNING CULTURE • • • • • • • • • Continuous learning at individual level Dialogue and enquiry at individual level Team learning Capture learning Empowerment Connect organization Leadership for learning Financial performance Knowledge performance Integration • Leadership– influences organizational culture— through strategy – —individual motivation – –performance or actions – –teaches new entrants – –components of culture