Introduction to RUP and Visual Modeling
advertisement

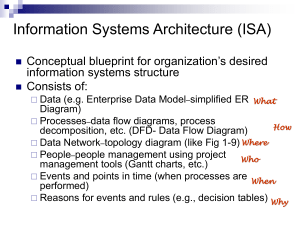
Introduction to RUP and Visual Modeling Month Day, Year RUP is Use Case-Driven Discipline Use Case Usage Project Management Basis for iteration planning Business Modeling Business use cases used to define and structure the business processes Requirements Where system use cases are formally defined and structured Analysis & Design Use cases are “realized” – define how use cases are performed by interacting objects in design model Implementation Use cases implemented by design classes Test Basis for Test Cases and Test Procedures – system verified by performing each use case Deployment Foundation for Users Guide Use Cases Assigned to Iterations Iteration 1 Iteration 2 Iteration 3 Product A Use Case 1 All scenarios Use Case 2 Use Case 3 All scenarios “Happy Day” scenario Alternative Flow 1 Alternative Flow 2 “Happy Day” scenario All Alternative Flows Product B Use Case 4 Use Case 5 Use Case 6 All scenarios All scenarios Use Case 3 Implementation Iteration 1 Iteration 2 Iteration 3 Iteration 4 Business Modeling Requirements Analysis & Design Implementation Test Deployment Configuration & Change Management Iteration 5 RUP – Model Overview Business Modeling System Use Case Modeling Design Modeling Who? Business Process Analyst System Analyst Designer/Developer What? Business Model System Use Case Model Design Model Where? Rose and ReqPro Rose and ReqPro Rose/XDE When? First 4 iterations All iterations Why? First 3 iterations Define business processes Identify points of automation Define functional requirements Start transition to design Define Components Integrate With Code RUP – Basic Steps Create Software Development Plan Create Project Model • Create visual sub-models – – – – Business Use-Case Model System Use-Case Model Design Model Implementation Model • Create requirements sub-model Knowledge Acquisition Model Develop Code Test Software Development Plan Create Vision and Features Identify Business/System Use-Cases Prioritize Business/System Use-Cases Create Iteration Plan and Schedule Create Supporting Process Plans and Guidelines Create Business Use-Case Model Identify Business Use-Cases Brainstorming major business processes Decompose using activity diagrams For each Business Use-Case create: Business Business Business Business Business Activity Diagrams Use-Case Diagrams Sequence/Collaboration Diagrams Statechart Diagrams Class Diagrams Create Business Use-Case Requirements Create System Use-Case Model Identify points of automation For each System Use-Case create: System Use-Case Diagrams System Activity Diagrams System Sequence/Collaboration Diagrams System State Transition Diagram System Statechart Diagrams Analysis Class Diagrams UI Design Diagrams/Mockups/Prototype Create Use-Case Requirements Create Design Model Import Rose Requirements Model into XDE Create Sequence/Collaboration Diagrams Transform Objects into Classes Create Action-level Activity Diagrams Create Design Class Diagrams Create Data Model/Database Create Implementation Model Integrate Code with XDE Model Forward engineer Implementation Classes Reverse engineer existing code and frameworks Write Code Unit Test Test Define Evaluation Mission Test Ideas Verify Test Approach Test & Evaluate Achieve Acceptable Mission Improve Test Assets Artifact Review Development Case Software Development Plan • Iteration 1 Plan – Plan – Schedule Business Modeling Guidelines Knowledge Acquisition Worksheet The Models Business Use-Case Model Identify the tasks, activities, roles and entities that accomplish business goals Identify Automation Points • Use-Cases (Automatable/ed Business Use-Cases) – Actors (Business Workers) – Entities (Business Entity) Use-Case Model Models User – System Interaction Clear, concise overview of the purpose and functionality of the system • All functional and non-functional requirements are mapped to at least one use-case and visa-versa The Model Design Model Use-Case Analysis • Objects Design Classes • Object Evolution • Identify Mechanisms and Elements Architectural Analysis • Assess Viability of Architectural Proof-of-Concepts Implementation Model Construct Architectural Proof of Concepts Prototype User-Interface Implement Classes The Models Deployment Model What where Test Model Test Cases • • • • Test Test Test Test Classes Scripts Data Results Model Evolution A process of working out or developing A process of change in a certain direction A process of continuous change from a lower, simpler, or worse to a higher, more complex, or better state Model Evolution Modeling Diagrams • • • • • Activity Sequence Collaboration Statechart Class – Use-Case – Object – Class Requirements • Multimedia Model Evolution Model Lineage Business Use-Case (BUCM) • Use-Case (UCm) – Design (DM) – Implementation (IM) – Deployment (DM) – Test ™ Activity Diagram – BUCM Primary Diagram for Requirements Specification Elements Activities • Actions Transitions Decisions Synchronizations States Activity Diagram – BUCM Activity Diagrams – BUCM Activity Diagrams – BUCM Swimlanes Integration of the division of activity between business actors / actors into the Business UseCase / Use-case activity Recognition of collaborating objects Activity Diagrams – BUCM Activity Diagrams – BUCM Activity Diagrams – BUCM Object Flows Integration of Business Entities / Entities into the Business Use-Case / Use-case activity Recognition of collaborating objects Sequence Diagrams - BUCM Show object interaction in a timebased sequence Establish the roles of objects Provide essential information to determine class responsibilities and interfaces Sequence Diagrams - BUCM Simplicity • Plain English Shows interaction between • Business Actors – Workers • Business Entities Sequence Diagrams - BUCM Collaboration Diagrams - BUCM Used to show how objects interact to perform a particular behavior Used to define and clarify the roles of the objects that perform a particular flow of events Better suited to depicting simpler interactions of smaller numbers of objects. Collaboration Diagrams - BUCM Collaboration Diagrams - BUCM Statechart Diagrams - BUCM Used To Model Dynamic Behavior Event-driven behavior • Are required for objects who call events and signal events to implement their operations State-dependent behavior • Are required for active objects whose behavior varies base on their state • Are not required for passive objects whose behavior does not vary with their state Statechart Diagrams - BUCM Statechart Diagrams - BUCM Class Diagrams – BUCM Models the static structure of the model Objects / Classes • Internal structure – Attributes – Operations Relationships to other classes Class Diagrams – BUCM Use–Case Diagram Class Diagrams – BUCM Object Diagram Class Diagrams – BUCM Activity Diagrams - UCM Simple Plain English Details interaction activity between Actors (Business Workers) System (Computer) Sequence Diagrams - UCM Simple Plain English Shows interaction between Actors (Business Workers) System (Computer) Other Diagrams - UCM Collaboration Statechart Class Use-Case Object Simple Plain English Activity Diagram – DM - Analysis Defining division of actions between objects for obtaining a particular result from the system Detailed • Actions • Requirements – Preconditions – Postconditions Sequence Diagram - DM - Analysis Defining interaction of objects for obtaining a particular result from the system Simple messages • Synchronization • Period Collaboration Diagrams - DM - Analysis Shows collaboration of objects for obtaining a particular result from the system Simple Messages Easy to Create F6 Layout Statechart Diagrams - DM - Analysis Shows achievable states of the objects within the system Simple Class Diagrams - DM - Analysis Show the static state of objects Structure • Simple attributes • Simple operations Relationships Activity Diagram – DM - Design Defining internal actions of an object to produce a particular result Sequence Diagram - DM - Design Defining interaction of objects for obtaining a particular result from the system Assignment • Simple messages become detailed messages / procedure calls to specific object operations • Programming Notation Collaboration Diagrams – DM - Design Shows collaboration of objects for obtaining a particular result from the system Detailed Messages / Procedure Calls to specific object operations Statechart Diagrams – DM - Design Shows achievable states of the objects within the system Detailed Internal Sub-States Class Diagrams - DM - Design Show the static state of classes Structure • Detailed attributes • Detailed operations Relationships • Detailed Traceability The ability to trace a project element to other related project elements, especially those related to requirements