flow of docs
advertisement

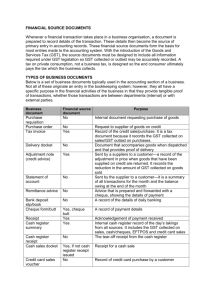
Flow of financial docs between businesses Order of financial docs 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Purchase order delivery note Goods received note Invoice Credit note Statement of account Remittance advice slip Cheque receipt Purchase order If you place an order for a new office chair then a purchase order would need to be completed I.e. purchase orders are made out when one business orders from another Purchase orders need to be checked for accuracy example Complete the purchase order with these details: you work for Mouse Matters You order 200 sq metres of blue mouse cloth, 20 m of black mouse cloth and 50 m of 2mm vinyl sheet Item codes are MC03, MC04 and V07 respectively Prices are £5.50, £5.50 and £6.60 respectively Ordering from Universal Fabrics, 4-10 Dickenson St, Battersea, London, SW11 ORT Order No is 2003/707 Supplier No is 97 Delivery is one week today I will sign as purchasing officer!! questions What happens if the following errors are present? 1. The suppliers post code is wrong 2. Suppliers name and address is wrong 3. Description of material is right but code is wrong 4. Price on the order is 2 less per item than stated in supplier’s price list 5. The form is not signed Delivery note Produced by suppliers of the goods and sent to the business customer with the goods After goods arrive, a staff member checks them and signs two copies of the delivery note One is kept and one returned to the supplier A signed delivery note means that everything is in order and the invoice can be sent If a large business uses its own specialist company to deliver goods the delivery note is known as an advice note example You must now complete the delivery note using the information from the purchase order Make sure you copy the order no correctly Likewise the customer no and address Also check item code and quantity Goods received note Each time an order is unpacked and checked a goods received note is filled in as a double check (may be because in first instance the delivery note was signed by reception) records what was delivered, when and by whom Needed by accounts to check details on invoice If there any differences or discrepancies the supplier is contacted immediately exercise 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. In groups of four discus the following and come to a group decision: What action would be taken if each of these occurred: Ten boxes of paper were crushed and damaged in transit Pink paper ordered instead of white The order stated 50 folders but 500 were delivered Only 15 ink cartridges were delivered instead of 20 invoice Sent form supplier to customer for payment for goods which have been delivered Prices added together to give total amount owing VAT will be calculated and added Obviously need to be checked for errors example Calculate the total invoice amount for mouse matters from universal fabrics given that VAT is 17.5% Fill in the blank invoice provided Credit note Used if customer overcharged or if goods are faulty Also used if wrong goods sent or the wrong amount sent Sometimes more may have been ordered than necessary. If the supplier agrees to take these back then a credit note can be used Statement of account Statements of account list or detail the transactions between two companies Usually sent out each month to all customers who owe money Three columns – the debit column shows amounts owed by the customer, the credit column shows amounts paid by the customer, the running balance column is calculated after each transaction Remittance advice slip Sent attached to the statement of account Divided by a perforated line so can be detached and sent back with cheque Obviously details should be checked on remittance advice with those on the statement of account Final details should be checked to tally with cheque written cheque Cheques are a convenient way of paying for large business transactions Also more secure than large amounts of cash Complete the blank cheque for the amount detailed on the statement of account for mouse matters i.e. for £3453.40 Common mistakes include: date incorrect, not signed, difference between amount written in words and numbers, alteration on cheque Minor alterations an be initialled receipt When cash is used a receipt will normally be issued Provides proof of purchase and allows for staff reimbursement Also provides details of VAT paid Two copies issued – one to customer, the other retained but the business Contains date, ref no, amount paid for each good, total and VAT added. Computerised systems: advantages Quick – instant in most cases Automatic Fewer mistakes Can chase up unpaid bills more easily No docs to lose Linked to other systems Can search customers easily Account nos allocated automatically More secure? Computerised systems: disadvantages Cost – can be expensive Input of data Staff training Hardware/computer failure Input errors – can be difficult to spot Can be inflexible