assure - Instructional Design & delivery / 2010 + Research methods
advertisement

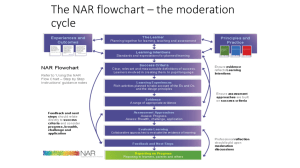
ASSURE Model QIM 501E/4 Rubiyatul Huda Md Ramli S-QM0028/10 Overview To become skilled instructors in today’s classroom is crucial to know when to use the instructional strategies and interactive multimedia. Robert Heinich and Michael Molenda of Indiana University and James D. Russell of Purdue University found that media and technologies is an effective systematic planning in teaching. Therefore, they have developed the ASSURE model in 1990's. What is ASSURE model? The ASSURE Model is: A procedural guide for planning and delivering instruction that integrates media into the teaching process A systematic approach to write lesson plans A plan used to help teachers organize instructional procedures A plan used to help teachers do an authentic assessment of student learning A model that can be used by all presenters How is it benefit learning process? The ASSURE Learning Model represents a manner of planning for student learning that will assure success. Planning learning sessions around this model will ensure effective and valuable learning for participants. The ASSURE Learning Model can be used for students at any grade level including adults in professional development. ASSURE is an acronym stands for… nalyze Learners tating Objectives elect Methods, Media & Materials tilize Methods, Media & Materials equire Learner Participation valuate and Revise Analyze Learners Before you begin the session, you must know your target audience. Understanding the learners is a key in preparing a successful learning session. Ask questions such as: What are all the prerequisites? Do the learners have the knowledge base required to enter the lesson? Why is the learner taking this course? What type of learning styles can motivate the learners? Once instructors understanding their learners, the planning may progress to the next element of the ASSURE model which is Stating Objectives Stating Objectives Stating the objectives of the session allows learners to understand ahead of time the purpose of the session. Things to keep in mind as you write your objectives are: Focus on the learner, not the teacher Use behaviors that reflect real world concerns Objectives are descriptions of the learning outcomes and are written using ABCD format Stating Objectives The ABCD’s of writing objectives Audience - Who is the audience? Behavior - The capability needs to be demonstrated as learner performance. Condition - Under what conditions are the learners to demonstrate the skills being taught? Degree - Degree to which the new skills must be mastered. Example: The QIM501E/4 students (Audience) will be able to give 100% (Degree) of what is ASSURE model (Behavior) when given a questions of learning models (Condition) Select Method, Media and Materials Once you know your students and have a clear idea of what they should get from the lesson, then you are ready to select the: Instructional Method that you feel most appropriate to meet the objectives. Media that would be best suited to work with your students. Media could be text, images, video, audio and computer multimedia. Materials that may help your students in mastering the objectives. It could be software programs, music, cd, images or equipment such as projector, TV, DVD, etc. Utilize Methods, Media and Materials Now it’s time to do your lesson and use the media and materials that you have selected. You should: Preview the material- never use anything in class you have not checked thoroughly Prepare the material- make sure you have everything you need and it all works Prepare the environment- set up the classroom so that whatever you’re doing will work well Prepare the learners- give the students on overview, explain how they can take this info and use it and how they will be evaluated then Provide the learning experience- teaching is simply high theatre. Showmanship is part of the instructors job. Teaching and learning should be an experience and not an ordeal. Require Learner Participation Remember, students learned best when they are actively involved in the learning. Describes how you want the student to participate in the class. Example: group work, presentations, discussions, games, etc. Avoid lecturing for an entire hour. Listen to your students and allow them to become alert of the content. Evaluate and Revise This last stage is often neglected but it is the most important one. Evaluate your students performance- Q&A session, forums, etc Evaluate media components effectiveness Evaluate instructor performance Revision ‘You are not a bad teacher if a lesson does not work. You are a bad teacher if you don’t reflect upon your lessons and work on revising elements of the lesson until your students become successful learners’. Summary A nalyze Learners S tating Objectives S elect Methods, Media & Materials U tilize Methods, Media & Materials R equire Learner Participation E valuate and Revise Conclusion By following the six steps of the ASSURE model, instructors are able to incorporate new technologies and technology- based media into their courses appropriately and effectively. Heinich, Molenda, Russell, Smaldino (2002) states. “All effective instruction require careful planning (p.54).” Incorporating the ASSURE Learning Model into the planning and delivery of instruction will ascertain successful delivery as well as learner outcomes. Heinich Molenda Russell Smaldino References Instructional Media and the New Technologies of Instruction by Heinich R., Molenda M., and Russel J., 4th edition, Macmillan, New York, 1993. Heinich.R, Molenda M., and Russel J. & Smaldino, S. (2002) Instructional Media and Technologies for Learning (7th Ed.). New Jersey, Merill Prentice Hall. Burnmark. L (2002). Visual Literacy, Alexandria: Association for supervision and curriculum. The Instructional Design Process Kemp J., Harper and Row, New York, 1985 Thank you