PERSONAL FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
advertisement

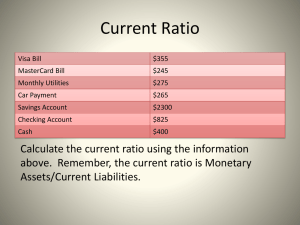
Chapter 2 PERSONAL FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT OBJECTIVES Describe the importance of personal financial management Identify the significance of money management and budgeting Identify the difference between gross income and net income Create a personal budget Recognize money wasters Identify debt and debt-management resources Identify wise use of credit Describe the importance of savings and investments Protect yourself from identity theft FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Personal financial management: the process of controlling your income and your expenses FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Income Income: money coming in Income may come from: Parents Grants Student loans Job After college and starting your new career your income most likely will increase FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Expense Expense: money going out Common college expenses include: Tuition, text books, supplies Housing Transportation Hobbies and entertainment Medical PERSONAL FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT AFFECTS WORK PERFORMANCE Personal finances impact all areas of your life Finances assist you in reaching life goals Keep debt under control Affect your work situation PERSONAL FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT AFFECTS WORK PERFORMANCE Maintain a positive credit report Use credit wisely Begin savings and investment now Protect yourself from identity theft Pay your bills YOUR PAYCHECK Do not overdo spending Now is the time to manage your money Create a budget to help you reach your goals Financial success begins with discipline and planning MONEY MANAGEMENT Budgeting Budget: a detailed financial plan used to allocate money for a specific time period Reflects your goals Controls and prioritizes spending Be honest and precise when creating a budget MONEY MANAGEMENT Cash Management Cash management is the key to good budgeting Record all transactions Carry a small amount of cash Reduce trips to the ATM MONEY MANAGEMENT Steps to Creating a Budget 1. 2. 3. 4. Identify goals Attach financial goals to personal goals Determine monthly income (money in) Determine monthly expenses (money out) Budget on a monthly basis Keep track of all spending Reduce money wasters MONEY MANAGEMENT Fixed expenses: expenses that do not change from month to month Flexible expenses: expenses that change from month to month Money wasters: small expenditures that you do not realize are actually using up a portion of your income DEBT MANAGEMENT Debt management involves: Debt Interest Net worth Assets Liabilities DEBT MANAGEMENT Debt, Loans, and Interest Debt: money you owe for borrowed funds Debt vs. expenses Debt includes a loan with interest Expenses include bills that come regularly Loan: a large debt that is paid in smaller amounts over a period of time and has interest added to the payment Interest: the cost of borrowing money This is extra money paid to the lender DEBT MANAGEMENT Total Net Worth Total Assets – Total Liabilities = Total Net Worth Assets: what you own Car, home, furniture Liabilities: an obligation to pay what you owe Car loan, home loan Net worth: the amount of money that is yours after paying off debt DEBT MANAGEMENT Steps to Get Out of Debt Do not create additional debt Prioritize your debt Pay off the smallest amount or the amount with the largest interest first Take the extra cash from a paidoff debt and apply it to the next debt on your priority list TALK IT OUT What are warning signs that you may be getting into debt? WISE USE OF CREDIT Manage Your Credit Managing credit is the best way to stay out of debt Do not abuse the privilege of credit and credit cards Spend wisely and pay off the balance each month Use credit only for items you can afford Avoid taking out loans TALK IT OUT Identify potential terms and conditions that you should consider before getting credit from a lender SAVINGS AND INVESTMENTS Begin saving now Put away funds for short-term goals or emergencies Rule of thumb: Have at least five months’ income saved for emergencies Have savings in a bank Determine if you should use a regular savings account or a Certificate of Deposit SAVINGS AND INVESTMENTS Begin investing now Opportunity to increase the value of your money Long term Involves risk Establish after you have a savings account IDENTITY THEFT Identity theft is when another individual uses your personal information to obtain credit in your name Prevent by: Disposing of any communication that contains your personal information Shred or cut up any mail and delete any electronic correspondence Keep copies of important information in a safe place IDENTITY THEFT Tips to Remember Do not give out your social security number over the telephone or Internet without verifying the authenticity of the company and individual requesting the information Document all important numbers and keep them in a safe place Practice good personal financial management Remove your name from credit card and marketing lists IDENTITY THEFT If You Become a Victim of Identity Theft File a police report Contact your bank, credit card companies, and cell phone provider Do not change your social security number, contact the Social Security Administration Fraud Department Contact the credit reporting agency fraud lines Document everything you do