The Formation of the Gospels
advertisement

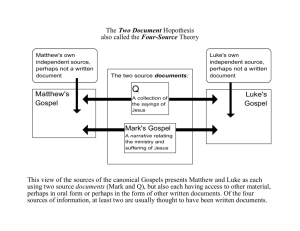
The Formation of the Gospels Some Chronological Order • Year 0 Jesus is born (but it’s probably more likely anywhere from 7 BCE to 4 CE) • Year 30 to 33 Jesus is crucified CE- Common Era The Genre Known as Gospel… • Meaning ‘good news’ • Deals solely with life and teachings of Jusus • Matt and Mark begin with birth • Mark and John begin with Baptism (beginning of ministry) • Late 60s – Early 70s Gospel of Mark is written for the persecuted Christian community in Rome, Christianity is illegal at this time • 70 The Romans destroy the Temple in Jerusalem, split between the Jewish community and the Jewish followers of Jesus • Late 70s - Late 80s The Gospel of Matthew is written for the Jewish followers of Jesus • Mid to Late 80s The Gospel of Luke is written for nonJewish Christians, Greeks living in an urban environment • 90 – 100 The Gospel of John is written for an unknown Jewish Community The Three Stages of the Development of the Gospels • Stage 1: The Lived Experience the life, death and resurrection of Jesus as experienced by the disciples • Stage 2: The Oral Tradition the stories and sayings of Jesus were kept alive orally among the followers of Jesus • Stage 3: The Written Gospels as the eye witnesses of Jesus began to die the members of the Christianity community began to put these oral stories into written form The Synoptic Gospels • Synoptic means “same view”, Mark, Matthew and Luke are called the Synoptic Gospels as they follow the same general pattern • Narrate same incidents, use similar phrasing (sometimes identical phrasing!) • Matthew and Luke seem to have had another source named “Q” - hypothetical source of sayings and stories found in Matthew and Luke but not in Mark • the Gospel of John in unlike the Synoptic Gospels, it has a unique writing style and contains passages found only in John’s Gospel • John’s gospel more concerned with Jesus’ divine nature and relationship to God, synoptics emphasize his messianic vocation and everyday religious and ethical matters. Matthew’s Gospel • Written in Antioch (modern day Turkey) around 80 CE • For a Jewish community who became first Christians • Warnings to stay united, refrain from judgement, accept sinners, form stable structure (church). Matthew’s Focus… • Jesus as ultimate teacher and authority on earth • Traced back through genealogy to King David • Portrayed as on who brings teachings/ethics of Moses to perfection (New Torah) The Sermon on the Mount: The Five Contrasts • In the Sermon on the Mount in Matthew’s gospel Jesus makes a series of contrasts between the law of the prophets and that of his teaching. • He doesn’t abolish the Torah, but rather gives it deeper meaning… In-class assignment… • Make notes on the 5 contrasts listed below as • • • • • • outlined in your text on pages 93-94. What did the original law of Moses say? How does Jesus give a new interpretation to the laws and customs of the Jewish ppl? 1. concerning anger 2. concerning adultery and divorce 3. concerning oaths 4. concerning retaliation 5. love for enemies