SE_-_FMEA - Rose
advertisement
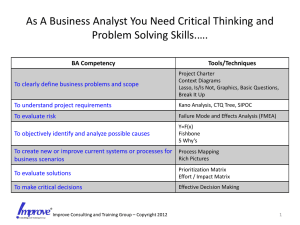
Systems Engineering – Risk Analysis with FMEA Special Topics Fishbone Chart FMEA 1 Risk/Failure Models At the ‘project’ level. At the system or device level. Common methods include Fishbone analysis or FMEA FMEA – Failure Modes and Effects Analysis 2 Fishbone Chart ‘Cause and Effect’ Analysis Create an Ishikawa or Fishbone Chart Head is ‘Problem’ – Skeleton are the ‘Causes’ Typical categories, 5M’s + E Man Machine Material Method Measurement Environment 3 Industrial Monitoring Sensor Create a Fishbone Chart for ‘Sensor Not Working’ 4 Analysis Tool – FMEA Failure Mode and Effects Analysis FMEA is an ‘enhanced’ Cause and Effect Analysis. (the 5M’s plus E) Do Fishbone Chart for Industrial Sensor. Apply FMEA to a Design or Processes at many levels. Systems often have many SPFs – single points of failure. 5 Design Tool – FMEA The Concept of FMEA: People Make Mistakes Products and Processes Fail Anticipate these errors and eliminate them with design or process changes !! 6 FMEA Example How many ways can a floppy disk be inserted ?? What design features make this possible?? 7 FMEA Steps -The traditional approach 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Team activity Select component, system, process step, etc. Identify possible failure modes. Identify causes of failure modes. Identify effects of failures. Estimate (1-10 ranking): 1. Occurrence – how often (1=not, 10=often) 2. Severity – how bad (1=not, 10=severe) 3. Detection – how easy (1=easy, 10=difficult) 7. Calculate RPN – ‘risk priority number’ 8 FMEA RPN example Occ 1 1 1 1 10 10 10 10 Sev 1 10 1 10 1 10 1 10 Det 1 1 10 10 1 1 10 10 RPN 1 10 10 100 10 100 100 1000 Comments No Problem No action, easy to detect. No action, not often or severe. Action Chronic problem, fix ? Chronic and severe, fix Chronic and customer issues, fix Bad, Bad, Bad – top priority Rules for OSD Values Threshold for Action – Varies Thresholds 55-100 (?) 9 From National Instruments 10 From National Instruments 11 Detection in Design or Manufacturing 12 POTENTIAL FAILURE MODE AND EFFECTS ANALYSIS Design FMEA System Subsystem Process FMEA Component Part Number Internal Use Only Page Design or Process Responsibility FMEA Number Prepared by Telephone # Original FMEA Date FMEA Revision Date Core Team Design Item or Process Function Requirements Potential Failure Mode Potential Effect(s) of Failure S e v C l a s s Potential Cause(s) / Mechanism(s) of Failure O c c Current Design or ProcessControls D e t R P N Recommended Actions Responsibility & Target Completion Date Actions Taken S e v O c c D e t . Many versions of this chart… 13 R P N Occurrence and Severity O and S are often the two critical factors and some analysis just looks at these two. 14 From Dieter Industrial Monitoring Sensor 15 16 FMEA Summary Combines ideas of ‘Cause and Effect’ chart, mistake proofing, and risk. Useful to identify and prioritize possible failure modes and fixes. Possible Fixes : High reliability components, De-rate components, Redundancy, Change the design. 17 FMEA - A Requirements Approach FMEA often starts with: Identify possible failure modes. How? – guess, experience, brainstorm, etc. Consider – Requirements are what the system is supposed to do. Counter-requirements (not being met) are failure modes. Use counter-requirements to populate the FMEA table. 18 Design FMEA Example 19 Design FMEA Coyote Hoist 20 Class Discussion – Process FMEA You are responsible for developing a process to stuff several hundred envelopes for a charity group. Each envelope is to contain three separate flyers and a cover sheet with the recipients name on it. After folding, the name must show in the cutout in the envelope. The final step is to seal and place stamps on the envelope for mailing. Develop a PFMEA* for this process. *Process FMEA 21