Overview of Operational Risk / Liability
advertisement

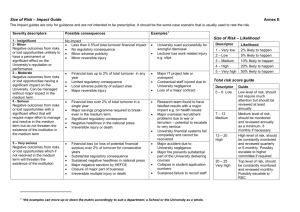
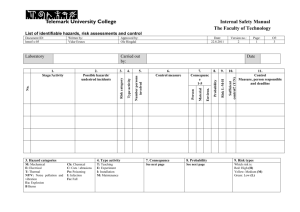
Overview of Operational Risk / Liability U.S. Maritime and Offshore Oil & Gas Industries What is risk? • • • Set of All Possible Hazards Likelihood of Occurrence of Hazards Consequence of each Hazard – what can go wrong? – how possible is it? – how bad can it get? RISK = PROBABILITY x CONSEQUENCE Hazards of Business • Operational: – Scope of Work • Indefinite • Beyond capabilities – Project management • • • • Resources Planning and logistics Execution Delays, productivity, competing projects • Reliance on third parties – Deliverables • Time • Quality – Changing expectations – Accidents • Property or equipment • People – Acts of God and Nature • Legal / Financial: – – – – Pricing risks Payment risks Delay costs Claims for defective deliverables – Termination risks Offshore Oil & Gas Activities • Exploration – – – – • Seismology Seafloor surveying / Mapping Drilling Transporting supplies, equipment or personnel Development – Drilling – Construction • Wells • Structures / facilities • Pipelines – Pipe-laying – Transporting supplies, equipment, or personnel • Production – – – – Operating structures / facilities On-site processing Transporting oil, gas, & gas condensates Transporting supplies, equipment, or personnel Maritime & Shipping Activities • Shipping – – – – – – • Logistics Managing inventory on-shore Loading Transporting, navigation, & pilotage Off-loading Customs Vessels / Assets – Newbuilding/commissioning – Operation and Maintenance – Salvage • Cargo – – – – • Bulk Container Human transport (Cruise ships) Special purpose (FPSO, LNG, Tenders, Tugs, etc.) Port – – – – Navigation Stevedoring Cranes Drydocking Probabilities & Consequences For Example: • Late arrival at designated location: – Probability: – Consequence: • Employee Error: – Probability: – Consequence: • medium to high - no material delay to others: no impact - delays overall project: $$ impact low to medium - not material error: no impact - material error: $$ impact - critical error: impact to life, property, or project viability Collision at Sea – Our negligence: – Probability: – Consequence: low - injury to customer personnel & property - injury to third parties or 3rd party property U.S. General Common Law concepts • Intentional Acts – Assault, Battery, Trespass, False Imprisonment, Defamation – Fraud, Wrongful Interference with Contract or Business Relationship – Intentional Infliction of Emotional Distress • Negligence – Acts that a person exercising ordinary care would not do under similar circumstances; or – Fails to do what a person exercising ordinary care would do under similar circumstances. • Negligence per se – Violation of a statute or ordinance that provides criminal penalty and that violation causes injury to another • Strict Liability in Tort – Abnormally Dangerous Activities – Product Liability More Specific Law concepts • Unseaworthiness – Ship owner’s duty to maintain its vessel in a seaworthy manner – Vessel’s equipment, masters, and members of the crew can render a vessel unseaworthy • Jones Act – Vessel owners’ liability for injuries to seamen • Oil Pollution Act – Responsible party liability for response costs to oil spills • U.S. Admiralty Law – Affect ship owners, cargo owners, marine insurers, and crew – Pertain to salvage claims, marine pollution, and collisions at sea • Anti-Indemnity Statutes of TX, LA, NM, & WY Risk Management - Key principles What can go wrong? How often? How big? • Risk Quantification – Likelihood – Consequence Is that OK? What can be done? Is it being done? • Risk Mitigation Measures – Risk acceptance criteria – Barrier identification and monitoring Mechanisms for Controlling Risk • Shift Risk to someone else – Buy Insurance – Seek Contractual Protections • Employ operational excellence – Employ the best people – Maintain state of the art operations – Provide best on-going training, and – Keep highly motivated