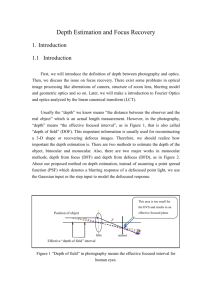
LCT
advertisement
MODULE 1 Introduction to Backward Design and Learner-Centered Teaching (LCT) Our Goal How to design engaging learning experiences that focuses on understanding? At the end of the course, faculty will be able to plan, design and implement an engaging course centered on students learning Learning Objectives • What is the difference between knowledge and understanding? • How the backward design differ from the traditional way? • How does course design affect student learning? • What are the benefits of backward design? • What are the stages of backward design? • How do they relate to each other? • How LCT differ from the traditional teaching? • What are the benefits of using LCT? • What are the LCT approaches? • What are the purposes of using LCT approaches? The Traditional Way Topic What is the course about? Resources and Instruction What do I need to help me to teach it? How should I teach it? Assessments How should I assess students? What is the PROBLEM? It is too Vague!! Choose a course and ask yourself: What is the purpose of the course? • Is it to cover the topics? • Is it to understand the book? Usually what professors do is to give the students as many information as possible Focus on cover the Knowledge What is the PROBLEM? Do Students really understand? Knowledge vs Understanding • Definitions and Concepts • Application to new and different • Where it can be applied situations • Limited application • Causes and consequences Follow a recipe Chef • May be successful if does exactly • Able to create new recipes what the recipes says • Able to predict what happens if an • Cannot cook without the recipe ingredient is added In summary, the problems are: • The course content is NOT aligned to the desired outcomes • The course may have too much content • Activities may not be aligned with the purpose of the course • It focuses on the content and teaching method, instead of student understanding (lack of application) What is the CONSEQUENCE? Next Slide Design affects learning How does course design influence student learning? Confusion to get the main point - Unrelated topics and the big idea. Students are not able activities to transfer the knowledge to other contexts Coverage approach encourages memorization – Knowledge will last for a short “cramming for the test” term. Students do not really learn How should the design be done? Next Slide The Backward Design Define Learning Objectives 1st Define Evidences of Learning and Assessment tasks 2nd Plan Learning Experiences 3rd 1 Learning Objectives What should the students know, understand and be able to do? • What is the point? • What is the Big Idea? • Why should students learn it? Evidences of Learning and 2 Assessment Tasks How will professors know if students achieved desired results? • How to measure understanding? • What look for? • How to evaluate the assessment results? 3 Learning Experiences What should students do to achieve the desired results? • What activities will help students to get the point? • What is the role of the professor? • How to engage students? 3 Learning Experiences What characteristics the learning experiences should have to help students to learn? Learner-Centered Teaching Teaching approach that: • Focuses on student learning • Encourages students to participate • Challenges students to think critically • Creates meaning from experience • Relies on multiples sources of learning and teaching • Uses examples grounded in real-life experience • Allows for creativity and discovery in and outside the classroom Why is it different? Next Slide http://www.ferris.edu/fctl/Teaching_and_Learning_Tips/Learner-Centered%20Teaching/LCOverview.htm http://www.ydae.purdue.edu/lct/mission.html The Traditional Teaching “It is a rain of information” Traditional Teaching vs LearnerCentered Teaching Behavioralism vs Constructivism Curriculum Begins with the parts of the whole. Emphasizes big concepts, beginning Emphasizes basic skills with the whole and expanding to include the parts Value Strict adherence to fixed curriculum is highly valued Pursuit of student questions and interests is valued Materials Textbooks and workbooks Primary sources of material and manipulative materials Learning base Repetition Interactive, building on what the student already knows Teachers Disseminate information Help students to construct their own knowledge SOURCE: http://www.thirteen.org/edonline/concept2class/constructivism/index_sub1.html The spotlight shifts from the teacher to the student! Behavioralism vs Constructivism Teacher’s role Directive, rooted in authority Teacher's role is interactive, rooted in negotiation and coaching Students Recipients of knowledge Builders of knowledge Assessment Through testing, correct answers Includes student works, observations, and points of view, as well as tests. Process is as important as product Knowledge Is seen as inert Is seen as dynamic, ever changing with our experiences Class Activities Students work primarily alone. Students work primarily in groups SOURCE: http://www.thirteen.org/edonline/concept2class/constructivism/index_sub1.html LCT Approaches Active Learning Makes the learning environment exciting! Encourages students to actively participate in class activities, promoting interest and increasing self-confidence Examples: • In-class discussion, debates, writing • Peer teaching or team working • Visual instruction: Videos, Demonstration • Games • Role-playing http://www.cat.ilstu.edu/additional/tips/newActive.php Inquiry Learning Understanding by questioning Encourages students to think critically and solve problems Examples: • Problem-Solving Activities • Case Study • Simulation to test different alternatives • Project Development http://thirteen.org/edonline/concept2class/inquiry/index.html Contextual Learning Learning in real-life situations Integrates classroom instruction with reallife situation and reflection. It applies knowledge in real-world , addressing community needs and turning students into responsible citizens Example: • Science class about pollution complemented with an activity of collecting trash in an urban area http://www.servicelearning.org/what_is_service-learning/service-learning_is/index.php Benefits Backward Design LCT • Engages students • Clear course objectives • Creates the habit of inquiring • Focus on the Big Ideas • Gives the opportunity to learn • Class activities and assessments from experience coherent with course objectives • Flexibility to adapt class activities to student style and interests Summary • Backward Design’s Essence is that a course must be designed around its objectives • Design stages: 1. Identify the big ideas and define objectives 2. Determine evidences of learning to measure if students achieved the objectives defined in stage 1 and the assessment tasks 3. Plan Learning Activities in order to help students to accomplish the course objectives • LCT is a teaching approach that improves student learning capabilities by encouraging them to engage in learning activities (Active Learning), think critically (Inquiry Learning), practice knowledge in real-life contexts, and become a responsible citizen (Contextual Learning) Learning Objectives • What is the difference between knowledge and understanding? • How the backward design differ from the traditional way? • How does course design affect student learning? • What are the benefits of backward design? • What are the stages of backward design? • How do they relate to each other? • How LCT differ from the traditional teaching? • What are the benefits of using LCT? • What are the LCT approaches? • What are the purposes of using LCT approaches? References • Backward Design Wiggins, Grant and McTighe, Jay. Understanding by Design. 2nd Edition. ASCD, Virginia, 2005. • Learner-Centered Teaching http://www.ydae.purdue.edu/lct/mission.html http://www.ferris.edu/fctl/Teaching_and_Learning_Tips/LearnerCentered%20Teaching/LCOverview.htm http://www.thirteen.org/edonline/concept2class/constructivism/index_sub1.html • Active Learning http://www.cat.ilstu.edu/additional/tips/newActive.php • Inquiry Learning http://thirteen.org/edonline/concept2class/inquiry/index.html • Contextual Learning http://www.texascollaborative.org/WhatIsCTL.htm http://www.servicelearning.org/what_is_service-learning/service-learning_is/index.php