A dichotomous key - CPO Science Texas Grade 8 Science TEKS
advertisement

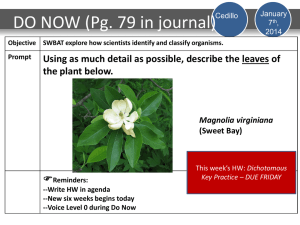
Dichotomous Keys: TEKS 7.11A To the teacher: • This CPO Science PowerPoint presentation is designed to guide you through the process of presenting the lesson to your students. The presentation uses a 5-E teaching model: Engage, Explore, Explain, Elaborate, and Evaluate. • The PowerPoint Slide notes indicate where you may want to bring in various lesson elements such as quizzes, readings, investigations, animations, and practice materials. Additional science background information is provided in the slide notes where appropriate. You can view these notes by selecting “View,” then “Normal.” You will see the notes pane at the bottom of the PowerPoint workspace. Additionally, the slide notes are available as a separate document, accessible from the lesson home page. • The slides that follow are intended for classroom use. Dichotomous Keys: TEKS 7.11A What kind of creature is that? Do you like to take walks through natural areas like prairies, woodlands, or along a riverside? Do you enjoy exploring tide pools, snorkeling, or scuba diving? Have you ever come across a creature you didn’t recognize? A dichotomous key can help you classify and identify living things. Dichotomous Keys: TEKS 7.11A A dichotomous key Dichotomous Keys: TEKS 7.11A Time to investigate! How do you create a dichotomous key? Dichotomous Keys: TEKS 7.11A Time for Practice! • Complete the lesson practice worksheet. Some hints for writing a dichotomous key: •Write the part name first, then the descriptive term (for example “Tail short and straight,” not “Short and straight tail”). •Start both choices in a pair with the same word. •Use measurements rather than vague terms like “big” and “little.” •Use characteristics that are true of all individuals in a group (for example, use fur color only if all individuals have the same color markings). Dichotomous Keys: TEKS 7.11A Whose shoes? A class dichotomous key What you will do: 1. Divide the class into groups of 8-12 students. Each person should remove one shoe and place it in the center of your lab table. 2. Separate the shoes into two groups based on a simple, easily-observed difference between them. Write a question that can determine the placement of each shoe into one group or the other. The question should be written so that it has only two answers, for groups a and b. 3. Examine the shoes in group a and repeat step 2 for this group. Keep repeating the process until the answer to a question leaves you with only one shoe. In this case, give the name of the person who owns the shoe. Repeat this process for the shoes in group b. Dichotomous Keys: TEKS 7.11A Whose shoes? A class dichotomous key Applying your knowledge: 1. 2. Take off your remaining shoe and place it under the table so you don’t give away the answer to the question, “Whose shoes?” Then pair up with another group. Switch tables with them, leaving behind the dichotomous key that you wrote. Randomly choose one of the other group’s shoes. Use the key that your partner group wrote to identify the chosen shoe. To whom did it belong? Did you get stuck at any step? Is this group’s key very different from yours? Dichotomous Keys: TEKS 7.11A Show what you know! • Try the lesson’s interactive quiz, or complete a quiz that your teacher can print out for you. • Hint: You might want to review your lesson reading piece one more time before trying the quiz.