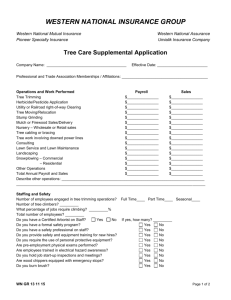
Herbicide Modes of Action
advertisement

Integrated Pest Management and Pesticides Bruce P. Alber, CF Wilbur-Ellis Company balber@wilburellis.com Pesticide definition • A product that prevents, destroys, repels, or mitigates a pest (FIFRA) • Christmas tree pesticides • Herbicides Fungicides • Insecticides Rodenticides • Deer Repellants How will you spray? Calibration is critical • How many gallons of mix per acre? • Constant walking speed, spray pressure, nozzle type • Different people walk different speeds • Careful calculation of pesticide per gallon of water depends upon calibration Calibration is critical • Proper pesticide rate per acre = • Enough product to control the pest • Too much product can damage trees and waste money • Too much product is illegal • Not enough product wastes money, doesn’t kill the pest, can cause weed escapes Pesticide use: IPM • Correctly identify the pest • Is the pest population above a level of damage concern? • Can an early treatment stop the population & reduce the need for repeated applications? • Is the pest life cycle at the succeptable time to treat? Don’t spray by the calendar! Are you a licensed applicator? - necessary for purchase & application of Restricted Use Pesticides Choosing a Christmas tree pesticide • Always read and follow all label directions • There must be specific recommendations for the site: Christmas trees • Conifer plantations? • Not forestry (Oust XP) • Not non-crop Modes of Action questions • Why does one pesticide control some species but not others? • You can tank mix some pesticides • Two or more herbicides in a tank • Mix an insecticide + a fungicide Herbicide activity types • Foliar spray: what stage of plant growth is best for control? Early leaf, bud stage, full extension, late summer? • Soil active spray: prevent weed seed germination Soil Active Herbicides: Conifers & Plant selectivity • Physical selectivity: • Soil active – solubility, soil adsorption breakdown half life • Herbicide location in soil vs. plant roots • Growth stage selectivity: • Weeds actively growing? • Seedling weeds? • Conifers dormant? What does this all mean to the grower on the ground? • Mix herbicides with different modes of action can broaden the weed control spectrum: • Westar: Oust + Velpar pre-mix • Mix your own: glyphosate + Atrazine • Understand the seasons of control by herbicide Herbicides and conifer safety • Conifer safety depends upon the herbicide • Dormant conifers are less likely to be damaged • Directed sprays reduce tree exposure and damage Prevent herbicide resistant weeds! • Rotate your herbicide use • Use different mode of action herbicides • Tank mix with different modes of action herbicides Insecticide & miticide use • Scout often to watch for insects & mites • When do they hatch? • What is the population trend? • What is the best growth stage for good control? • Weather forecast: hot weather can cause a mite population explosion Miticide modes of action • What life stage does the pesticide kill the insect or mite? Egg, larva, adult? • Does the miticide kill the adults or adults and the eggs? • Does the pesticide kill beneficial insects too? Fungicide use • Scout your fields for needle discoloration, fungal fruiting bodies from last year • When will the trees be harvested? • Most fungicide treatments are 2-3 years before harvest. Especially the harvest year! Questions, comments? Bruce Alber, CF Wilbur-Ellis Company BAlber@wilburellis.com 503-799-1428