Ch25 - Accounting
advertisement

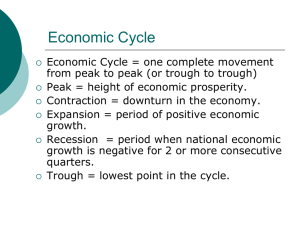
Short-Term Business Decisions Chapter 25 Exercises Short-Term Business Decisions In-Class Exercises: Exercise No. E25-17 Page 1568 Sales Mix Decisions Short-Term Business Decisions Exercise E25-17: Ned’s Beach Hut stocks its drink case each morning. The drink case has 115 linear feet of refrigerated drink space. Each linear foot can hold either six 12-ounce cans or three 20-ounce bottles. Products are as follows: Yummy Time Yummy Time Pretty Pop 12-ounce can 20-ounce bottle 20-ounce bottle Selling Price…………. $1.45 ………….. $1.75 …………… $2.30 Cost…………………… 0.15 ………….. 0.35 …………… 0.65 Ned’s Beach Hut’s monthly fixed costs include: Hut rental…………….. $ 360 Refrigerator rental….. 80 Ned’s salary…………. 1,500 Total fixed costs……. $1,940 Ned’s Beach Hut can sell all the drinks stocked in the display case each day. Requirements: (1) What is Ned’s constraining factor? What should Ned stock to maximize profits? (2) Suppose Ned’s Beach Hut refuses to devote more than 75 linear feet to any individual product. Under this condition, how many linear feet of each drink should Ned’s stock? How many units of each product will be available for sale each day? Short-Term Business Decisions Short-Term Business Decisions Short-Term Business Decisions End of Exercise Short-Term Business Decisions In-Class Exercises: Exercise No. E25-18 Page 1569 Outsourcing Decisions Short-Term Business Decisions Exercise E25-18: Fiber Systems manufactures an optical switch that it uses in its final product. The switch has the following manufacturing costs per unit: Direct materials…………………$ 9.00 Direct labor……………………… 1.50 Variable overhead…………....... 5.00 Fixed overhead…………………. 9.00 Manufacturing product cost…. $24.50 Another company has offered to sell Fiber Systems the switch for $18.50 per unit. If Fiber Systems buys the switch from the outside supplier, the manufacturing facilities that will be idled cannot be used for any other purpose, yet none of the fixed cost are avoidable. Requirement: Prepare an outsourcing analysis to determine whether Fiber Systems should make or buy the switch. Short-Term Business Decisions Short-Term Business Decisions Short-Term Business Decisions End of Exercise Short-Term Business Decisions In-Class Exercises: Exercise No. E25-20 Page 1569 Sell or Process Further Short-Term Business Decisions Exercise E25-20: Naturalmaid processes organic milk into plain yogurt. Naturalmaid sells plain yogurt to hospitals, nursing homes, and restaurants in bulk, one-gallon containers. Each batch, processed at a cost of $800, yields 600 gallons of plain yogurt. Naturalmaid sells the one-gallon tubs for $7 each and spends $0.16 for each plastic tub. Naturalmaid has recently begun to reconsider its strategy and wonders if it would be more profitable to sell individual-size portions of fruited organic yogurt at local food stores. Naturalmaid could further process each batch of plain yogurt into 12,800 individual portions (3/4 cup each) of fruited yogurt. Naturalmaid would sell each individual portion for $0.54. Packaging would cost $0.07 per portion, and fruit would cost $0.11 per portion. Fixed costs would not change. Should Naturalmaid continue to sell only the gallon-size plain yogurt (sell as is) or convert the plain yogurt into individual-size portions of fruited yogurt (process further)? Why? Short-Term Business Decisions Short-Term Business Decisions Short-Term Business Decisions End of Exercise