Chemical Regulation
Chemical Control in Plants:
Hormones
–
–
–
–
allow for
Growth
Reproduction
Tropisms
Hormones found in roots, stems, and seeds
Role of Hormones
Auxin:
– a hormone that allows for cell division and
growth.
– An unequal distribution of auxin, causes a
tropism.
Tropism:
– Response to stimulus.
– Ex. Light phototropism
Water hydrotropism
Tropism in plants
Phototropism
Less
auxin on light side
More auxin on dark side
Positive phototropism
– (grows towards light)
Aim: What is the function of the
human endocrine system?
Chapter 15- Endocrine System
Composed
of glands located throughout
the body that secrete hormones
Endocrine Glands:
– Produce hormones
Chemical
messengers
Specific- affect different target cells of the body
– These glands are ductless.
Human Endocrine System
Exocrine
Glands: contain ducts which
secretions pass through. Ex) Salivary
glands
Endocrine Glands:Ductless.
– Hormones are secreted directly
into the bloodstream.
– The hormones maintain
homeostasisREGULATION.
Nervous System vs. Endocrine System
Nervous System
Endocrine System
Maintain Homeostasis
Chemical
Neurotransmitters
Fast Response
Quick Response
Maintain Homeostasis
Chemical Hormones
Slow Response
Lasts Longer
Aim: What are some of
the glands of the Human
Endocrine System?
Hypothalamus:
Area of the brain that connects the N.S. to the
endocrine system.
Stimulates the pituitary gland.
Types of Glands:
Pituitary
– “master gland”
– produces hormones that turn on other glands.
– Location: within brain
– Hormones Secreted:
Growth Hormone
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
Hypothalamus
Pituitary Hormones:
Thyroid stimulating Hormone- TSH
Stimulates the thyroid gland to produce
thyroxin.
Follicle stimulating Hormone- FSH
Stimulates the ovaries and testes.
Growth Hormone- GH
Increases growth of bones and muscles.
Leutinizing Hormone- LH
Stimulates ovulation to occur in females.
Thyroid gland
Thyroid Gland
Thyroxin
Hormone
Contains iodine
Regulates metabolism
Location: In Neck
Parathyroid gland
Parathyroid Glands
Parathormone
Regulates calcium metabolism
Location: Small pairs of glands in neck
Adrenal gland
Adrenal Glands
Adrenaline (epinephrine) Hormone
Helps the body in emergency situations
Increases- heartbeat, respiration, blood sugar
levels.(Adrenaline Rush)
Pancreas: Islets of Langerhans
Location: group of cells located in the pancreas.
Insulin Hormone
Is needed to allow sugar to enter our cells.
Lowers blood sugar (glucose) levels.
When does insulin get produced in our bodies?
After we eat b/c the sugar needs to go into our
cells.
Pancreas
Pancreas-Islets of Langerhans
Glucagon Hormone
Opposite of insulin
Increases blood sugar (glucose) levels.
Causes sugar to be released from the liver when
blood sugar levels are too low.
When is glucagon produced in our bodies?
When we skip a meal- blood sugar is too low.
Testes
Gonads-
Sex Glands
In the gonads, sex cells develop into
gametes (sperm cells and egg cells).
Male gonads: Testes
– Testosterone Hormone
– Develops secondary sex characteristics
– Deep voice, facial hair.
Ovaries
Female
gonads: Ovaries
Estrogen Hormone
– Develops secondary sex characteristics
– Broad hips, hair growth
– Regulates menstrual cycle
Progesterone
Hormone
– Regulates menstrual cycle
Testes/ Ovaries
Regulation of Hormone
Secretion
Hormones are not secreted at a constant rate.
Hormone secretion varies with the body’s needs
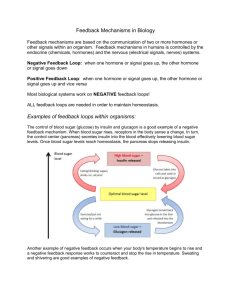
This is accomplished by FEEDBACK.
Negative feedback:
– Opposes original change
– Most common - maintains homeostasis
1.
2.
3.
4.
Negative Feedback –
Mechanism that maintains
homeostasis
High Blood Sugar
Pancreas secretes insulin
Blood Sugar lowers to homeostasis
Pancreas stops secreting insulin
Negative Feedback regulates
homeostasis like a thermostat regulates
temperature
Malfunctions of the Endocrine
System
Diabetes:
Caused by an insulin deficiency (Pancreas doesn’t make enough)
Results in an elevated blood sugar level.
To manage this, medication or injections of insulin must be taken
Goiter:
Enlargement
of the thyroid gland.
Caused by a hyposecretion of thyroxin.
Also caused by an iodine deficiency.
Giantism
Dwarfism
Dwarfism
How Hormones Work
Hormones
are specific!!!!
Hormone and target cell receptors fit
together like a “lock and key”