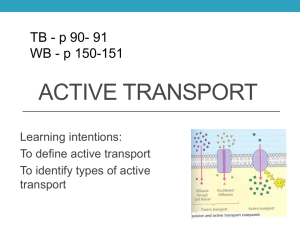
Cell transport with the environment
advertisement
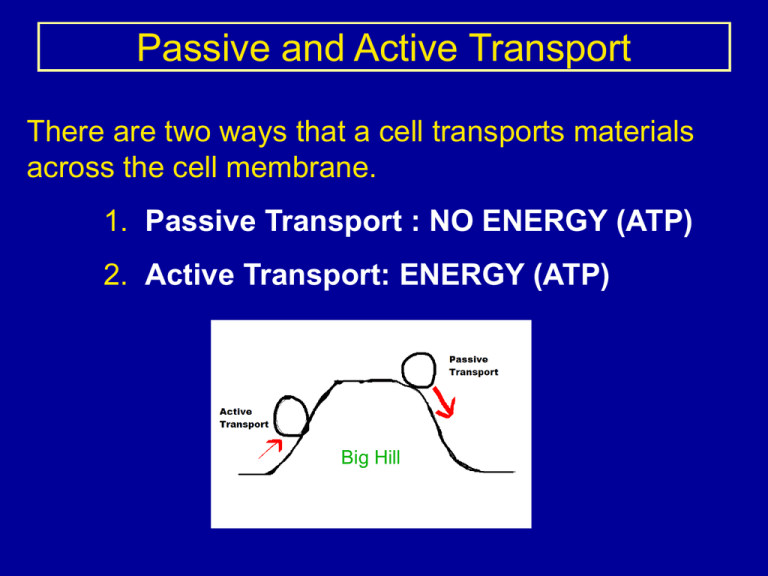
Passive and Active Transport There are two ways that a cell transports materials across the cell membrane. 1. Passive Transport : NO ENERGY (ATP) 2. Active Transport: ENERGY (ATP) Big Hill Passive and Active Transport Passive Transport: Moving materials across the cell membrane without using energy (ATP) There are two kinds of passive transport: 1. Diffusion: Dissolved gasses, small particles 2. Osmosis: WATER ONLY Passive and Active Transport Diffusion: The process where particles such as oxygen, carbon dioxide and sugar move from areas of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Passive and Active Transport Osmosis: The process of diffusion involving only the water molecule. Water molecules still move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration without the involvement of ATP. Passive and Active Transport Active Transport: Moving materials across the cell membrane by using energy (ATP). Particles such as sodium and potassium ions often need the help of ATP to pass through the cell membrane. Active transport occurs when the particle is moved against the gradient. Low concentration High concentration Passive and Active Transport Active Transport – Exocytosis and Endocytosis: Sometimes particles are too big to move through protein channels in the cell membrane. The cell then uses exocytosis and endocytosis to move materials out of the cell and into the cell. Exocytosis Wastes (toxins) Hormones Endocytosis Bacteria Proteins Passive and Active Transport Active Transport – Exocytosis occurs when particles need to be moved from inside the cell to outside the cell. Exocytosis Wastes (toxins) Hormones Exo = EXIT Passive and Active Transport Active Transport –Endocytosis: Endocytosis occurs when cells need to move large particles from the outside to the inside of the cell. Endocytosis Bacteria (White blood cells) Proteins Endo = INTO Passive and Active Transport Active Transport –Endocytosis and Exocytosis: Passive and Active Transport Follow up activity using clay models Teal = Cell Membrane and Nucleus Light pink = Molecules to be transported Purple = Arrow showing passive transport (No energy) Hot pink = Arrow showing active transport (Energy) Passive and Active Transport Use the following slides to help you make a flipbook detailing active transport, passive transport, diffusion, osmosis, endocytosis and exocytosis. You will use this flipbook to study for your test. Passive Transport Diffusion from inside the cell to outside the cell: Low Concentration Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide, sugar High Concentration Passive Transport Diffusion from outside the cell to inside the cell: High Concentration Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide, sugar Low Concentration Passive Transport Osmosis from outside the cell to inside the cell: High Concentration Low Concentration WATER ONLY Passive Transport Osmosis from inside the cell to outside the cell: Low Concentration High Concentration WATER ONLY Active Transport Active transport of a large molecule: Low Concentration Low Concentration ATP ATP High Concentration High Concentration Low Concentration ATP High Concentration Active Transport Active transport exocytosis: ATP ATP ATP Active Transport Active transport endocytosis: ATP ATP ATP Photosynthesis Respiration Worksheets 1. Chapter 4 worksheet from Friday. Thirty total questions. 2. Chapter 4 Reinforcement worksheet (front and back)