Demographic Transition
advertisement

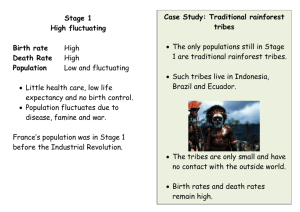
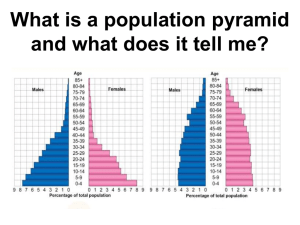
What do you think these cartoons are saying? J. Gathorpe-Hardy Hanel, Germany Population Change Outputs Inputs Births Natural Increase Deaths Total Population Immigrants Migration Emigrants The total population of an area is the balance between 2 forces of change: natural increase and migration Natural increase is the balance between birth rates and death rates World Population Changes Global Natural Increase Doubling Time This map shows how long it will take for countries to double their population if it continued to grow at the present rate Demographic Transition Model Stage 1 Natural Increase In Population Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Total Population Natural Decrease In Population Birth Birth Rate Rate Death Rate Stage 1 High Fluctuating • Low population Stage 1 Birth Rate – Increasing very slowly Death Rate Total Population • • • • High birth rate High death rate Ethiopia/Niger UK: pre-1780 Reasons for Stage 1 High Fluctuating Stage 1 Birth Rate Death Rate Total Population • Little access to birth control • Many children die in infancy so parents have more to compensate • Children are needed to work on the land • Some religions encourage large families • Death rates are high due to disease, famine, poor diet, poor hygiene, little medical science Stage 2 Early Expanding Stage 2 Birth Rate Total Population Death Rate • Population growing at faster rate • High but decreasing birth rate • Decreasing death rate • Sri Lanka/Bolivia • UK: 1780-1880 Reasons for Stage 2 Early Expanding Stage 2 Birth Rate Total Population Death Rate • Improvements in medical care • Improvements in sanitation and water supply • Quality and quantity of food produced improves • Transport and communications improve movements of food and medical supplies • Decrease in infant mortality Stage 3 Late Expanding Stage 3 Total Population Birth Rate Death Rate • Population, still increasing, but rate of increase slowing down • Decreasing birth rate • Low death rate • Uruguay/China • UK: 1880-1940 Reasons for Stage 3 Late Expanding Stage 3 Total Population Birth Rate Death Rate • Increased access to contraception • Lower infant mortality rates so less need for bigger families • Industrialisation and mechanisation means fewer labourers required • As wealth increases, desire for material possessions takes over the desire for large families • Equality of women means they can follow a career rather than just staying at home Stage 4 Low Fluctuating Stage 4 Total Population Birth Rate Death Rate • High population, almost stable • Low birth rate • Low death rate • Canada/USA • UK: post-1940 Reasons for Stage 4 Low Fluctuating Stage 4 Total Population Birth Rate Death Rate • Rates fluctuate with ‘baby booms’ and epidemics of illnesses and diseases • Reasons for Stage 4 have improved and it stabilises Demographic Transition Model Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Total Population Natural Increase In Population Natural Decrease In Population Birth Rate Death Rate Ethiopia/ Niger UK: pre-1780 Sri Lanka/ Bolivia UK: 1780-1880 Uruguay/ China UK: 1880-1940 Canada/ USA UK: Post-1940 Is there a Stage 5? ? ? ? Stage 5: Depleting Population Problems • What problems do you think there could be with the model? • It does not include the influences of migration • It assumes that all countries will go through the same pattern • There is no time scale • Reasons for birth rates and death rates are very different in different countries • And finally, is there a stage 5? The End? Population Pyramids • The population structure of a country is how it is made up of males and females of different ages. • The common method to show the structure is by a population pyramid. • This diagram is made up by putting two bar graphs (one for male, one for female) side by side. • From this you can read off what percentage of a population is of a certain gender and age range. Developing Countries • This population pyramid is wide at the base, which means there is a large proportion of young people in the country. • It tapers very quickly as you go up into the older age groups, and is narrow at the top. • This shows that a very small proportion of people are elderly. Developed Countries • This shape is typical of a developed country. • It is narrow at the base, wider in the middle, and stays quite wide until the very top, as there is a sizable percentage of older people. • Note that there are more old women than men. Ever-Changing Populations UK Population – 1995-2050 Different Population Pyramids Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Stage 5 Population Sketches Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Stage 5 Urban v. Rural Structures Differences between Models Demographic Transition Model Population Pyramid Model •Drawn as a line graph •Doesn't show male and female populations •Shows total population as a separate line •Gives details of countries in stages •Shows the relationship between birth and death rates and how these affect total population •Only one diagram necessary to show all stages •Drawn as a bar graph •Shows male and female population proportions •Total population is shown as the total area of the graph •Shows greater detail about the populations at each stage •4/5 diagrams necessary to show all stages Population Pyramid for …?…