DAC PowerPoint Template - richmedia
advertisement

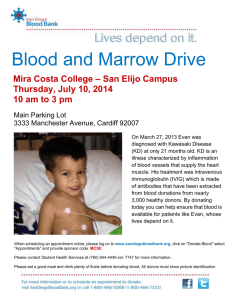
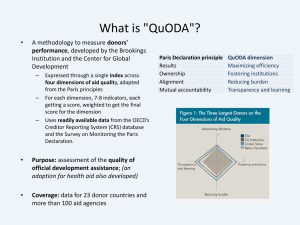
Advancing innovative development and aid strategies in the Asia Pacific Sydney, 16-18 June 2010 The Paris Declaration on Aid Effectiveness – MDG8 in progress Marjolaine Nicod OECD-DAC The Paris Declaration on Aid Effectiveness A key contribution to enhancing global partnerships for development (MDG-8): – Why aid effectiveness matters – What it is about – Where we are – What’s next 2 Why does aid effectiveness matter 3 Change ….? Why Change? 4 Too little from too many donors? A world map of donor fragmentation • • 5 4000 aid relationships globally (of 46 donors in 151 countries) 50% of all relations represent only 5% of aid Problematic aid management at country level 800 Vietnam (752) 750 700 650 600 Niger (569) Indonesia (590) 550 Lao PDR (569) 500 Madagascar (509) Number of donor missions: 14 420 missions in 55 countries in 2007 What is the aid effectiveness agenda? 7 The Aid Effectiveness Journey Dili Declaration on peacebuilding and statebuilding (2010) Monterrey Consensus (2002) 8 Rome Declaration on Harmonisation (2003) Paris Declaration on Aid Effectiveness (2005) Accra Agenda for Action (2008) Bogota Statement on South South Cooperation (2010) Korea HLF (2011) Where are we today? 9 Paris Declaration: 56 commitments and 12 indicators (targets for 2010) 2005 10 2010 Targets 1 Operational Development Strategies 2 Reliable Public Financial Management Systems 3 Aid flows are recorded in countries' budgets 42% 4 Technical assistance is aligned & coordinated 48% 5a Donors use country PFM Systems 40% 45% [80%] 5b Donors use country procurement systems 39% 43% [80%] 6 Donors avoid parallel PIUs 1817 1832 7 Aid is more predictable 41% 8 Aid is untied 75% 9 Donors use coordinated mechanisms for aid delivery 43% 10a Donors coordinate their missions 18% 21% 40% 10b Donors coordinate their country studies 42% 44% 66% 11 Sound frameworks to monitor results 7% 12 Mechanisms for mutal accountability 22% 17% 75% 22% 36% 50% 48% 85% 50% 611 1601 71% 46% 88% 47% 9% 26% [100%] 66% 38% 100% 60% What has changed? • A widely accepted set of norms and benchmarks • Monitoring in place to hold donors and developing countries accountable • Country-led evidence-based dialogue • Growing body of evidence • Fragility and conflict at the forefront • A more inclusive and fairer global partnership for development 11 What’s next? 12 How to keep political momentum? • Demonstrate value for money and accountability - progress against the Paris Declaration/AAA commitments and changes at country level • Make aid make a difference - use evidence to identify which principles matter most – and focus on these • Get ‘back to basics’ - aid effectiveness is about doing, not talking • Step up the multi-stakeholder and inclusive dialogue CSOs, Parliaments, private sector, middle income countries • Decide on an aid effectiveness framework to 2015 - based on evidence of what matters for development, and with a monitoring process to hold partners to account 13 14