auditing sales and cash receipts
advertisement

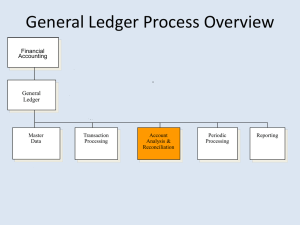
TOPICS Nature of revenue/receipt cycle Flow of information Auditor’s assessment of control risk Audit of internal2 control for sales, cash receipts Computer auditing, sampling, tests of controls Assurance, consulting services 2 NATURE OF REVENUE/RECEIPT CYCLE Goods, services sold to customers in exchange for future promises to pay Cash collected from customers 3 Sales Order 1 Credit / Customer Service 2 REVENUE CYCLE (SUBSYSTEM) Cash Receipts/ Collections 6 Shipping 3 Billing/ Accounts Receivable 4/5 DFD of Sales Order Process REVENUE/RECEIPT CYCLE Flow of Information Customer order received Sales order prepared Price, quantity, goods, terms Shipping document Identifies goods shipped Contract between seller, carrier Sales invoice (bill) Customer remittance advice Returned with payment from customer 6 SELLER’S DOCUMENTS Sales order Identifies goods ordered, price, quantity, terms, etc. Shipping document (bill of lading) Identifies good shipped Contract between seller & carrier Sales invoice Formal notice to customer of amount & payment terms Customer remittance advice Returned with payment 7 CONTROLS FOR CREDIT SALES Multicopy, prenumbered sales order prepared Customer credit reviewed, approved Authorized copy sales order accompanies goods from Inventory Control to Shipping Goods received in Shipping compared with sales order; shipping document prepared Common carrier provides receipt for goods shipped Shipping document, approved sales order sent to billing for preparation of invoice, daily sales summaries Invoice copy sent to General Accounting for recording 8 CASH COLLECTION Process Checks by mail listed, endorsed List copy to Accounts Receivable with remittance for posting List copy with checks to Cash Receipts Dept. for daily deposit Sales returns separate from cash collection Uncollected accounts Reviewed for credit limits, aged, written off as necessary 9 INTERNAL CONTROL & RISK Controls Risks Authorization Credit risk, uncollectible accounts Shipment, billing not timely Prenumbered shipping documents Recording controls Items recorded in improper amounts, accounts Theft Restricted access 10 ASSESSING CONTROL RISK Obtain Understanding Document the client’s system Flowchart, questionnaire, narrative Perform transaction walk-through Identify control activities Test controls to reduce control risk below maximum Assess control risk 11 TESTS OF CONTROLS Sales, Collection Provide a reasonable degree assurance that employees comply with management’s procedures Sales Properly authorized, executed, recorded Cash collections Cash receipts recorded, deposited promptly Returns, uncollectible accounts Proper authorization, recording 12 CONTROL RISK Shipping Major risks Unauthorized shipment Fictitious or related parties Goods properly shipped, not billed, recorded 13 TESTING CONTROLS: Shipping Select random sample shipping documents Examine sample for authorized sales order & agreement Trace sample shipping documents to invoices (completeness) Trace invoices to sales journal, A/R ledgers Trace invoices to inventory records 14 CONTROL RISK Billing Major risks Bills sent but goods not shipped Bills not properly prepared, recorded 15 TESTING CONTROLS: Billing Select sample invoices from Billing dept. Verify unit prices & mathematical accuracy Trace invoices to shipping documents (existence/occurrence) Trace invoices to sales journal, A/R ledgers Trace invoices to inventory records 16 CONTROL RISK Recording Periodic summaries not prepared or not prepared correctly 17 TESTING CONTROLS: Recording Review evidence of procedures for Reconciliation daily sales summaries with sales journal totals Periodic reconciliation A/R trial balance with general ledger control Scan sales journal for unusual transactions, large amounts Verify mathematical accuracy sales journal for selected periods; trace postings to general ledger 18 CONTROL RISK Cash Collection, Deposit Risk of embezzlement, deposit into improper accounts 19 TESTING CONTROLS: Cash Collection & Deposit Cash collection Surprise basis: take control bank deposits Compare total checks to total deposit slip Compare check details to cash receipt records & A/R ledger Determine timeliness Deposits Interim: compare deposits CRJ with bank statements Trace CRJ to general ledger 20 CONTROL RISK Sales Returns, Allowances Risk that credit memoranda Not approved Not properly recorded 21 TESTING CONTROLS: Sales Returns & Allowances Test details random sample credit memoranda Receiving reports Perpetual inventory records Entries A/R ledger & general ledger Review credit register for unusual items 22 CONTROL RISK Uncollectible Accounts Risk that account write-offs Properly authorized Properly recorded 23 TESTING CONTROLS: Uncollectible Accounts For written-off entries: Select sample Trace to authorization Trace to posting Review write-offs for unusual entries 24 ASSESSING CONTROL RISK 2 Questions Are controls effective? Can controls be relied upon? If answer is yes to both Assess control risk below maximum Assess detection risk above minimum Restrict substantive tests of sales, receivables, cash 25 PRELIMINARY OPINION ON INTERNAL CONTROL Auditor must form opinion on management’s assessment of internal control over financial reporting based on Reports of internal auditors Auditor’s tests of controls Substantive audit tests 26 TESTS OF CONTROLS Deduction Management 3 Critical questions Does Accounts Receivable monitor deductions? Does Account Operations approve deduction inquiries Does senior management review decisions made by Accounts Receivable, Account Operations? 27 TESTS OF BILLING CONTROLS An Example Randomly select sample sales invoices Verify unit prices, clerical accuracy Trace details of invoices to shipping documents Trace sales invoices to inventory records 28