Customer Decision Making

Customer Decision Making
A good salesperson does not just sell a product’s FEATURES. They sell . . .
BENEFITS
How do you know what
BENEFITS the customer wants or needs?
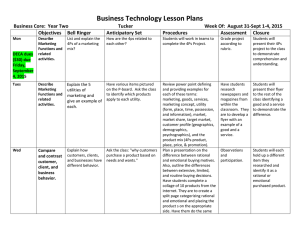
Lesson Objectives: You will be able to
• describe the difference between rational and emotive customer motives to buy.
• identify a few rational and emotive motives for making purchases.
• describe extensive, limited and routine decision making processes.
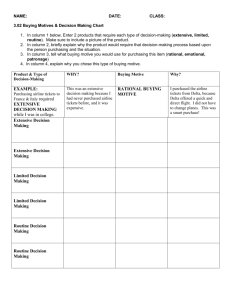
A rational buying motive is a conscious, factual reason to buy.
• dependability
• time savings
• money savings
• convenience
• comfort
• health or safety
• recreational value
• service
• quality
dependability
My Mountain Bike time savings money savings convenience quality service recreational value comfort health & safety
An emotive (emotional) motive is a feeling experienced by a customer through association with a product.
• social approval
• recognition
• power
• love
• affection
• prestige
social approval recognition power prestige affection love
Both rational and emotional motives may be present in the same purchase.
Michelin tires
Rational motives
• Safety
• Wide tread for traction
• 80,000 mile warranty
• Quality name brand
Emotional motives
• Loved ones
• look MACHO on my truck
• I can afford expensive tires!
• I buy only the BEST!
Guess which buying motive . . .
Products
• Ford Focus
• Ferrari
• Levis jeans
• Hilfiger jeans
• Keds
• Air Jordans
Customers
• Teenager buying a car
• YUPPY buying a car
• Parent buying a car
• Retiree buying a car
How much thought and consideration does a customer put into a buying decision?
• Amount of previous experience with the product or company
• How often the product is purchased
• Amount of information necessary to make a wise buying decision
• Importance of the purchase to the customer
• Perceived risk
• Time available to make the decision
Degrees of decision making
Extensive decision making
• little or no information known
• high perceived risk
Limited decision making
• has purchased before but not regularly
• moderate degree of perceived risk
• needs some information
Routine decision making
• purchased before
• high prior experience
• low risk
Remember!
Brand loyalty will move the decisionmaking process from
Extensive toward the
Routine.
On a clean sheet of paper . . .
• Write down four (4) products for each of the decision-making levels
– Extensive
– Limited
– Routine
• Using your product, write down four (4) detailed rational and four (4) emotional buying motives that a customer may experience with your product.
Due before the end of class today.
Homework
Complete end-of-chapter exercises A & B
Due tomorrow at beginning of class