Later People of the Fertile Crescent
advertisement

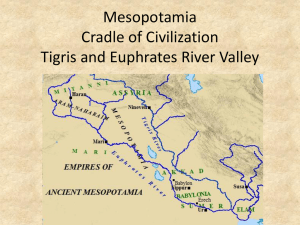
Later People of the Fertile Crescent Chapter 3; Section 4 72-77 Fertile Crescent Empires Hittite Babylonian Kassite Fertile Crescent Empires Phoenician Assyrian Chaldean Later Empires of the Fertile Crescent Babylonian Hittites Kassites Assyrians Chaldeans Phoenicians Later Empires of the Fertile Crescent Babylonian Hittites Kassites Assyrians Chaldeans Phoenicians •Conquered Sumer •Hammurabibrilliant leader, ruled for 42 years •Hammurabi’s Code-1st law code written down, 282 laws, and eye for an eye concept •Created Irrigation Projects and improves tax system •Hammurabi dies and empire declines (weakens) •Captured Babylon •Empire in presentday Turkey •Used Chariots and fire arrows around the battlefield •Hittite rule did not last long •Kassite people captured the Hittite people after their king was assassinat ed •Ruled for 400 years •In 900 BC, they started to conquer all of the Fertile Crescent •STRONG, ORGANIZED ARMY •They spread terror •Demanded heavy taxes and punished those who resisted •Built roads to link parts of the empire •Messengers on horseback to deliver messages •Series of wars weakened the empire •Destroyed Nineveh and the Assyrian Empire and rebuilt Babylon •Nebuchadnezz ar was their most famous ruler •Nebuchadnezz ar build one of the wonders of the world “Hanging Gardens” •Admired Sumerian culture and studied their language •Present-day land of Lebanon •Wealthy trading society •Cedar and Purple Dye •Mountains blocked their trade routes, so they turned to the sea •Tyre-harbor •ColoniesCarthage •Had fast ships •Traveled around Mediterranean •World’s 1st alphabet Tips: Remember this Sentence Sam and Bob heard kangaroos and chimpanzees playing. Sam (Sumer) and (Akkad) Bob (Babylonian) heard (Hittites) kangaroos (Kassites) and (Assyrians) chimpanzees (Chaldeans) playing (Phoenicians) Main Idea 1: The Babylonians conquered Mesopotamia and created a code of law. • Hammurabi was Babylon’s king. • During his rule, Babylon became the most important city in Mesopotamia. • Hammurabi’s Code was a set of 282 laws he created that dealt with almost every part of daily life. Hammurabi Babylon’s king and the city’s greatest monarch, or ruler of a kingdom or empire Brilliant war leader who brought all of Mesopotamia into his Babylonian Empire • Oversaw building and irrigation projects and improved the tax system • Developed a set of laws that was written down for all to see Hammurabi’s Code • Hammurabi wrote down 282 laws which contained some ideas still found in laws today. • Specific crimes brought specific penalties. • Social class was taken into account. It was a greater crime to injure a rich man than a poor one. • It was unique not only because of how thorough it was, but also because he wrote it down for all to see. Main Idea 2: Invasions of Mesopotamia changed the region’s culture. • Armies battled for control of fertile land. • Different peoples ruled Mesopotamia. – Hittites – Kassites – Assyrians – Chaldeans • Each group affected the culture of the region. The Hittites & Kassites The Hittites were the first to master ironworking, so they made the strongest weapons of the time. They used the chariot, a wheeled, horse-drawn cart, which allowed them to move quickly around the battlefield. They were taken over by the Kassites after their king was assassinated. The Kassites ruled for almost 400 years. The Assyrians • The Assyrians had a strong army that used chariots and iron weapons. • They spread terror before battles by looting villages and burning crops. • Assyrian kings ruled their empire through local leaders who each governed a small area. • The local leaders demanded heavy taxes. The Chaldeans • The Chaldeans attacked the Assyrians when they were weak and destroyed their empire. • Nebuchadnezzar rebuilt Babylon into a beautiful city that had the famous Hanging Gardens. • They admired the Sumerian culture, studied their language, and built temples to Sumerian gods. • Babylon became a center for astronomy. Main Idea 3: The Phoenicians built a trading society in the eastern Mediterranean region. Resources • Prized Cedar trees for timber • Accessed the sea for trade • Built great harbors Expansion of Trade Trade • Sailed ships around the Mediterranean Sea • Founded several new colonies along the trade routes • Became wealthy Alphabet • Recorded their activities • Made writing much easier for everyone • Is the basis for the English language Chapter 3 Summary Chapter 3-4 Questions When did Hammurabi become Babylon’s king? How did Hammurabi conquer Mesopotamia? Why would it have been helpful for people to have the law code written down? 4. Why did the Hittite Kingdom come to an end? 5. What military advantages did the Assyrians have? 6. How do you think the use of chariots by Hittites affected the opposing army’s foot soldiers? 7. How did the Assyrians rule their empire? 8. What advances did the Chaldeans make? 9. Where did Phoenician ships sail? 10. Why was the Phoenician alphabet an important development? 11. What led the Phoenicians to create a successful sea trade? 1. 2. 3.