File - PhysicallyEducated.com
advertisement

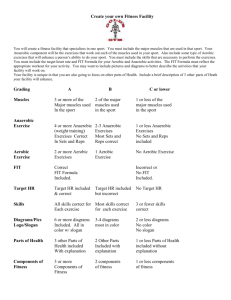
Section 13.1 The Importance of Physical Activity Instructions: On your notebook paper, write 5 exercises that you can think of that would be considered aerobic and 5 exercises that would be considered anaerobic. Aerobic Exercises Anaerobic Exercises 1. 1. 2. 2. 3. 3. 4. 4. 5. 5. Section 13.1 The Importance of Physical Activity Objective Describe the five types of physical activity. Section 13.1 The Importance of Physical Activity Types of Physical Activity • Physical activities can be classified as 1) aerobic exercise or 2) anaerobic exercise. • Strengthening and endurance activities can be further classified as 1) isometric exercise, 2) isotonic exercise, or 3) isokinetic exercise. Section 13.1 The Importance of Physical Activity Aerobic Exercise • Ongoing physical activity that raises your breathing rate and heart rate is called aerobic exercise OH exercises bik). • (ehr Aerobic increase the amount of oxygen that your body takes in and uses. Section 13.1 The Importance of Physical Activity Aerobic Exercise • Examples: Swimming, running, brisk walking, and cross-country skiing are all forms of aerobic exercise. Section 13.1 The Importance of Physical Activity Anaerobic Exercise • Intense physical activity that lasts for a few seconds to a few minutes is called anaerobic exercise. • Most anaerobic exercises develop muscular strength, muscular endurance, or flexibility. Section 13.1 The Importance of Physical Activity Anaerobic Exercise • Examples: Lifting weights, doing push-ups, and sprinting are examples of anaerobic activities. Section 13.1 The Importance of Physical Activity Isometric Exercise • Isometric exercise (eye suh MET rik) is an exercise in which muscles contract but very little body movement takes place. • If you do isometric exercises on a regular basis, the muscles you use will become stronger. Section 13.1 The Importance of Physical Activity Isometric Exercise • Examples: planks, pushing against a wall, climbing, mountain biking and motocross (grip and upper body strength), Judo, wrestling, gymnastics and horseback riding Section 13.1 The Importance of Physical Activity Isotonic Exercise • Isotonic exercise (eye suh TAHN ik) involves contracting and relaxing your muscles through the full range of a joint’s motion. • Through repetition of isotonic exercises, you can develop muscular strength and endurance. Section 13.1 The Importance of Physical Activity Isotonic Exercise • Examples: Pull-ups, exercises with free weights (such as biceps curls, bench press, leg extensions, incline press, squats) Section 13.1 The Importance of Physical Activity Isokinetic Exercise • In isokinetic exercise (eye soh ki NET ik) muscles contract at a constant rate. • These exercises are often used as therapy to rebuild muscle strength after an injury. Section 13.1 The Importance of Physical Activity Isokinetic Exercise • Examples: fitness machines (stationary bike, bench press machine) Section 13.1 The Importance of Physical Activity Class Activity – Charades Instructions: Students will volunteer to act out a physical activity. The class will try to guess which physical activity you are doing and will raise their hand to answer. Students will then have to decide which type of physical activity the student acted out and which components of health-related fitness is involved in performing that activity. Section 13.1 The Importance of Physical Activity Closure – Types of Physical Activity Crossword Puzzle Instructions: Without using your notes, complete the crossword puzzle given. You have 5 minutes to complete this assessment of how much you learned from today’s lesson about the 5 Types of Physical Activity. Make sure you turn your crossword puzzle in before leaving class today. Section 13.1 The Importance of Physical Activity Quiz – Types of Physical Activity 1. An ongoing physical activity that raises your breathing and heart rates. 2. Intense physical activity that lasts for a few seconds to a few minutes. 3. Exercise in which muscles contract but very little body movement occurs. 4. Exercise that involves contracting and relaxing muscles through the full range of their joint’s motion. 5. Exercise performed with machines that ensure muscles contract at a constant rate.