Slide 1 - National Council of State Boards of Nursing
advertisement

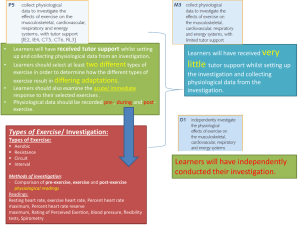
The Investigatory Process 2013 NCSBN IRE Conference Rene Cronquist, J.D., RN Minnesota Board of Nursing Director of Practice and Policy Tools in the Regulation tool box Regulation uses a variety of mechanisms – tools, if you will, to carry out is mission of public protection What’s in your tool box? Statutes, Rules, Regulations, Case Law, Policies, Advisory Opinions Program approval/Accreditation Credentialing Licensure Registration Certification Information/Data What’s in your tool box? Big tools: Enforcement, compliance, discipline, investigation, remediation The right tool for the job Knowing which tool to use depends on what you are trying to do. In the context of investigation, are you: Deciding if the complaint/report is within the authority of your agency? Gathering factual information to determine whether the complaint has merit? Gathering information for another group or agency to make decisions? Determining what action is most appropriate based on the available information? Complaint process Intake Investigation Board Proceedings Board Actions Reporting and Enforcement Complaint process – another view Intake Investigation Board Proceedings Board Actions Reporting and Enforcement Details Intake Complaint receipt Initial review Intake tools Sources of complaints Mandatory and permissive report Board as a source of complaints; self reports; Nursys Methods of submitting complaints Screen for jurisdiction Thresholds, triage, prioritizing, coding Tracking mechanisms Intake Investigation Results of Investigation Investigation tools An effort to learn the who, what, where, why, when and how of the allegations Methods: Record gathering Employment Medical records of nurse or patient Pharmacy and Prescription drug monitoring program records Controlled substance inventory logs Court records and police reports School records Reports from other agencies Bank records Investigation tools Forensics Evaluation of licensee (CD, mental health, neuropsych) Drug testing Computers (home & work PCs, cell phone, EHR access) Drugs (assay of syringe contents, analysis of automated dispensing machine history) Interviews/Written statements Licensee Patient/victim Witnesses Supervisor and coworkers Collateral contacts Investigation tools Written statements/affidavits Recordings Surveillance videos Audio recordings as evidence Audio recordings of interviews Site visits Other records Employer policies and procedures Databanks (Nursys, HIPDB/NPDB) Investigation results Reports Formats, templates Know your intended audience and all possible readers Recommendations; Determining next steps Challenges Coordinating investigation with other agencies Peer review protection of records Out-of-state records Destroyed records Uncooperative witnesses Unreliable or incompetent witnesses Uncooperative or unlocatable licensees Your favorite tools Results of Investigation Board proceeding & action Board proceedings & actions Informal processes Stipulated agreements Formal process Contested case hearings; administrative hearings Standard of proof must be met (clear and convincing vs. preponderance); Board typically has burden of proof Appeals of Board decisions Emergency/temporary proceedings Authority -- usually limited – to take action against a license before a hearing on the merits Miscellaneous Board proceedings & actions Conclude the complaint without action (dismissal) Referral to a non-disciplinary monitoring program Non-disciplinary action (letters of concern, admonishment, reprimand, Agreements for Corrective Action) Disciplinary Action Board proceeding & action Reporting and Enforcement (Compliance monitoring) To Report or Not to Report Is the action public? Is the action reportable? Nursys HIPDB/NPDB OIG Compliance monitoring Terms and Conditions Probationary terms Reports from the nurse Reports from the nurse’s supervisor Audits – documentation, med administration Additional education Maintain sobriety, attend support groups Drug screens Restrictions/Limitations Supervision required Restricted access to controlled substances Limitation on work hours or locations Compliance monitoring Non-compliance Failure to comply, violations of the order; new allegations Process used to address non-compliance depends on terms and conditions of the order and individual state laws More tools Checklists Tracking mechanisms Report forms Audits Randomizing drug screens Challenges and policy questions How much information is enough? How to manage sometimes competing priorities? Efficiency, cost containment, timely resolution of cases, appropriate resolution of cases. How do we measure quality and effectiveness? Resources NCSBN Networking opportunities Conferences Website materials CE offerings CLEAR FARB NADDI Interviewing technique training Dean Benard, Benard & Associates The Reid Technique Thank you! Rene Cronquist, J.D., RN Minnesota Board of Nursing 2829 University Ave SE #200 Minneapolis MN 55414 (612) 617-2198 Rene.Cronquist@State.mn.us www.NursingBoard.state.mn.us