Mecca - Spokane Public Schools
advertisement

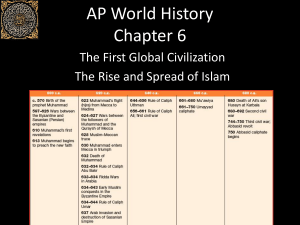
Rise and Spread of Islam Interaction Between Humans and the Environment • Arabia was an inhospitable desert. • Bedouin culture developed over centuries. • Clan rivalries were fierce. • Shaykhs led the clans. • Mecca was an important trade city. • Umayyad clan dominated politics and trade in Mecca. • Medina was an oasis and contested by two bedouin clan and three Jewish clans. Medina Mecca Development and Interaction of Cultures Before the 7th century Arabia consisted of polytheistic tribes. As Arabs migrated to Byzantine and Sasanian empires, they encountered monotheistic religions. Muhammad created a new religion. Based on the Qur’an The Sixth Pillar Jihad –struggle • Greater Jihad is personal struggle. • Lesser jihad/jihad of the sword or armed struggle against unbelief and evil After Mohammed: Civil War • Disagreement over who should succeed Mohammed • Sunni sect argued new leaders should be chosen by a committee and should be the best candidates • Shia (Partisans of Ali) argued that Ali (Mohammed’s son-inlaw) should “inherit” the leadership Name of Allah in Calligraphy Schism with Islam Sunni Shi’a Supported by Umayyads Supported Ali Early Caliphs • A hastily gathered group of leaders proclaimed Abu Bakr ( Mohammed’s father-in-law) the next “caliph” • Abu Bakr was the father of Aisha – youngest and most favored wife of Mohammed • A caliphs was both a religious and civil leader Men and women were separated in prayer . Far more so than with Buddhism or Christianity, the initial spread of Islam was both rapid and extensive. And unlike the other two world religions, Islam gave rise to a huge empire, ruled by Muslim Arabs, which encompassed many of the older civilizations of the region Dar al Islam: “The House or Community of Islam” • Early Muslim society was a syncretic blend of Arab, Persian, Greek, and Indian society – Transformed the societies it absorbed – Islam had political, social and religious significance • Ruled 3 core economic areas – Middle East – Central Asia and China ( used the Silk Roads) – Indian Ocean Basin (maritime trade routes) Umayyad Dynasty 661- 750 CE • Umayyads were a prominent merchant class • Brought stability to Islam after the civil war between partisans • Umayyads were more of a “secular” dynasty – Pursued military conquest – Adopted Byzantine bureaucratic techniques to rule ever expanding empire • Established their capital at Damascus (in Syria) Great Mosque at Damascus, Syria Islam Spreads to Spain North African Muslims (“Berbers”) invaded and conquered southern Spain Islamic Spain (Moorish) was known as Al-Andalus It was not until Ferdinand and Isabella won back Granada did Columbus get the money to travel to the new world. The Islamic empire was at its height during Umayyad Famous “Moorish” Mosque in Cordoba, Spain The Abbasid Dynasty 750 CE -1258 The Abbasid Palace Abbasids made their capital at Baghdad in present day Iraq • The secular ways of the Umayyads had scandalized devout Muslims • Rebellion in Persia brought Umayyad dynasty to end • Abu al Abbas founded new dynasty that lasted until Mongols toppled it 1258 CE • Abbasids were less interested in military conquest and more content to administer the empire they inherited Abbasid Dynasty • Abbasids adopted Persian administrative techniques to govern empire – Regional governors represented the caliph (religious leader) in affairs – Vizier ( chief counselor) role was also adopted from Persian administrations • Ulama – pious scholars developed public policy in accordance with Qur’an Abul Abbas- Charlemagne’s gift from Harun al Rahsid New Networks of Trade & Exchange Merchants on camel caravans traversed Dar-alIslam and spread religion, and ideas as well as trade goods • Umayyad and Abbasids created zones of trade, exchange and communication that extended from Spain to India • Islamic merchants used camel caravans across the deserts. • Seasonal monsoon winds facilitated trade and exchange across Indian Ocean Basin • Paper making was stolen from the Chinese when an Arab army defeated a Chinese army at Battle of Talas River in 751 The Muslim Sultanate of Delhi • Invading Muslims established Islamic rule in northern India • The Delhi Sultanate refers to the various Muslim dynasties that ruled northern India from 1206 – 1526 CE • Muslim traders had a lively trade with India Qutbuddin Aibak, founder of one of the five Dynasties that ruled the Delhi Sultanate Development and Transformation of Social Structures • Caliph – Religious and political successor • Mawali – Muslim converts • Dhimmi – “people of the book” • Ayan – Land-owning elite umma Dhows Sailed the Indian Ocean Basin Indian Dhows used Muslim invented Lateen Sails to maneuver cross winds Islam: A “World System” • Islam transcends the concept of “state” • Islam is a world view: science, mathematics, medicine, literature, inter-regional trade routes • Along with Byzantine empire (which it eventually took over in 1453) it was the economic and political anchor of the post-classical middle eastern world – Umayyad Caliphate ( centered at Damascus) – Abbasid Caliphate ( centered at Baghdad) – Safavid of Persia (Iran) – Mughal Empire ( India) What are Islam’s Legacies ? • Muslims adopted & adapted Greek, Persian & Indian traditions and techniques • Muslims were responsible for preserving Greek & Roman literature, drama during Europe’s “dark ages” • Islam transcended “state” and large numbers of conquered peoples converted to Islam • While Arabic was language of religion (Qur’an), theology, philosophy and law………… Persian became language of literature, poetry, history