Welch
advertisement
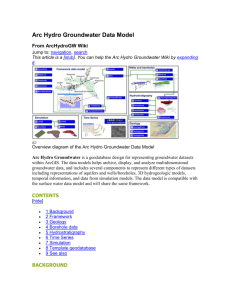
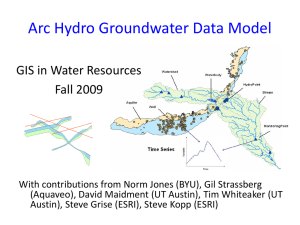
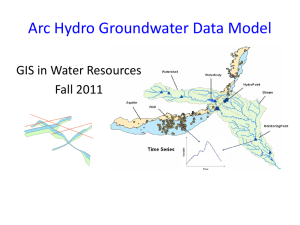
ADAPTING THE ARC HYDRO DATA MODEL AND TOOLS TO A HYDROGEOLOGIC FRAMEWORK KITSAP PENINSULA, KITSAP, MASON AND PIERCE COUNTIES, WASHINGTON Wendy Welch PRESENTATION OUTLINE • Background • Research Problem • Proposed Methods • Geology Component • Borehole Component • Hydrostratigraphy Component • Conclusion • Projected Timeline • Anticipated Results • References BACKGROUND U.S. GEOLOGICAL SURVEY PROJECT S • USGS WA Water Science Center • Collects statewide hydrologic data (surface and groundwater data) • Performs water resource investigations (quality and quantity) • Work with federal, state and local agencies to solve water issues BACKGROUND HYDROGEOLOGIC FRAMEWORK • Definition: 3D model of the subsurface hydrogeologic units; water bearing aquifers and confining units • Needed for greater understanding of groundwater characteristics and flow directions. • Created by incorporating hydrogeologic and geologic maps, well logs with borehole data and cross sections. • Can be used for conceptual understanding or as input to numerical flow and transport simulation models BACKGROUND CURRENT METHODS • Surficial geologic maps compiled from variety of sources and merged into one shapefile. • Well data is retrieved from USGS NWIS (National Water Information System) database • MS Excel is used to store and manage well data • Well data is exported to shapefile format for plotting in Arc Map • Cross sections are made using A Prime’s CrossView in Arc Map • Hydrogeologic unit (HGU) assignments are made and edited in Excel tables • Surfaces representing the tops of each HGU are interpolated using Spatial Analyst tools • Final surfaces viewed in CrossView BACKGROUND CASE STUDY • Kitsap GW study • ~790 sq. miles • 20 1:24k geologic maps merged • >2,000 wells with lithologic information • 11 unique hydrogeologic units (aquifers and confining units) BACKGROUND ARC HYDRO DATA MODEL COMPONENT S • Arc Hydro Groundwater (AHGW) is a data model and related set of tools for managing, analyzing and visualizing groundwater information • Originally Arc Hydro was developed for sur face water resources. Expanded to include groundwater data • Gil Strassberg developed AHGW data model for doctoral studies at University of Texas at Austin Center for Research in Water Resources • Data model components: Image from Strassberg and others, 2010 BACKGROUND ARC HYDRO GROUNDWATER TOOLS 3 Toolsets developed by Esri and Aquaveo TM that use groundwater information from the data model as a foundation. • Groundwater Analyst • Import existing data into AHGW data model (geodatabase) • Edit attributes • Manage well data • Subsurface Analyst • Visualizing borehole logs • Creating and editing cross sections • Making 2D sections and volumes • MODFLOW Analyst • Create, archive and visualize MODFLOW models * not used for this project RESEARCH PROBLEM NEED FOR STRUCTURE • USGS allows for a lot of freedom for scientists to select methods and software that are appropriate for their individual projects. • Benefits: • Fosters curiosity in new technology. • Flexibility in determining best fit. • Challenges: • Difficult to coordinate users if communication is limited. • Inefficient process if individuals are researching new software independently. • Hard to share or incorporate data from other projects, even within one science center if data is not managed in a universal structure RESEARCH PROBLEM WHY AHGW? • Helps to standardize groundwater and hydrogeologic datasets and maintain organization • Geodatabase design is scalable – elements can be added or removed but the basic structure remains • Data model and tools work within ArcGIS - the standard GIS software of the USGS • Tools have 3D visualization and analytic advantages over current methods PROPOSED METHODS AHGW GEODATABASE • Geodatabase can be imported from tool in Groundwater Analyst • Gdb can be customized to meet project needs • Coded value domains for certain attributes are used to increase efficiency and maintain integrity of data when editing • Features are related using HydroID attribute PROPOSED METHODS GEOLOGY COMPONENT • Geologic maps form starting point for hydrogeologic studies • Represent geologic units at land surface • Kitsap project required compilation and edgematching over 20 1:24,000 geologic map quadrangles • When final shapefile of surficial geology is complete, data is loaded into the GeologyArea polygon feature class of the AHGW geodatabase PROPOSED METHODS BOREHOLE COMPONENT • B o re h oleLog t a bl e • Represents vertical data along borehole • Relates to HydroID of Well feature class using WellID • Data is loaded from MS Excel into BoreholeLog table using data loader wizard PROPOSED METHODS HYDROSTRATIGRAPHY COMPONENT • Hydrogeologic units are assigned to different elevations along borehole. • HGU assignments are the basis for further analysis and processing • Subsurface Analyst tools used to create: Image from Strassberg and others, 2010 • • • • Cross sections Top surfaces Fence diagrams Volumes CONCLUSION PROJECTED TIMELINE • December 2012 • Import current data into geodatabase • January 2013 • Create cross sections and assign HGU top elevations to wells • Interpolate HGU surfaces from tops • February 2013 • Build 3D fence diagrams and volumes in Arc Scene • March- April 2013 • Finalize report and presentation for Symposium CONCLUSION ANTICIPATED RESULT S • Adapting a universal system design will: • Improve data management • Increase efficiency • Expand ability to communicate 3D concepts • Presentation of results • WA Hydrogeology Symposium, April 2013 REFERENCES Jacobsen, L. J., Glynn, P. D., Phelps, G. A., Orndorff, R. C., Bawden, G. W., & Grauch, V. J. S., 2011, Chapter 13: U.S. Geological Survey - A synopsis of three-dimensional modeling: Illinois State Geological Survey Circular 578, p. 69-79. Reilly, T.E., 2004, A Brief History of the contributions to ground water hydrology by the U.S. Geological Survey. Ground Water, v. 42, no. 4, p. 625-631. http://pubs.usgs.gov/article/groundwater/2004/vol42.html [Accessed November 21, 2012] Strassberg, G., Jones, N.L. and Lemon, A., 2010, Arc Hydro Groundwater Data Model and Tools: Overview and Use Cases: Aqua mundi – Journal of Water Sciences, p. 101-114. http://www.acquesotterranee.com/rivista/arc-hydro-groundwater-data-model-and-toolsoverview-and-use-cases?language=en [Accessed October 15, 2012] Strassberg G., Jones, N.L. and Maidment, D.R. 2011. Arc Hydro Groundwater: GIS for Hydrogeology. ESRI Press. Redlands, CA, 160pp. Welch, W.B., 2012, GEOG 897D Final Project; Arc Hydro Groundwater Data Model and Geodatabase Design, The Pennsylvania State University.