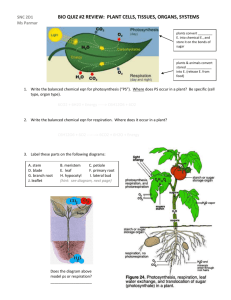
Practical 3: general anatomy of the leaf
advertisement

Variation in leaf anatomy SPECIMENS: 1. Ligustrum TS 2. Pinus TS 3. Nerium oleander leaf TS 4. Amaranthus. TS 5. Nymphaea TS 6. Zea mays TS (+) Ligustrum palisade xylem this leaf is bifacial fascicular cambium phloem spongy mesophyll (-) ©CEJB’99 ©CEJB’99 Adaxial epidermis palisade xylem phloem Spongy mesophyll stoma Ligustrum Pine needle epidermis stoma hypodermis transfusion tissue mesophyll endodermis Transfusion tissue resin canal ©CEJB’99 transfusion tissue protoxylem metaxylem secondary xylem tracheids fascicular cambium secondary phloem primary phloem endodermis transfusion tissue ©CEJB’99 Nerium oleander minor vein Stomatal crypt ©CEJB’99 CO2 /O2 exchange Amaranthus (pigweed) grows in disturbed farmland. Grown as ornamental ground cover. This is a C4 dicot. (+) Kranz mesophyll Bundle sheath cells ©CEJB’99 (-) Guard cell (stoma) (+) KMS BS ©CEJB’99 (-) bulliform cell adaxial Kranz mesophyll MX MX ©CEJB’99 abaxial stoma Bundle sheath Zea mays is a C4 grass. So like Amaranthus, the vascular bundles are surrounded by a BUNDLE SHEATH and exarch to this, the KRANZ MESOPHYLL TS Zea mays, vascular bundle protoxylem Bundle sheath metaxylem phloem epidermis ©CEJB’99 (+) Nymphaea sclerieds Intercellular air spaces ©CEJB’99 (-) And so, we come to the end of this short talk, time to move on and think of larger things that stand with their feet in the ground and have Little green bits sticking out up the stalk.. Redwood, Yosemite California ©CEJB’76