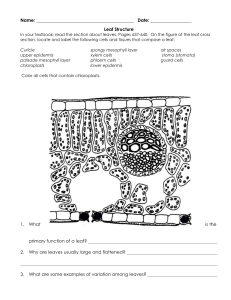
Why the mesophyll cell sizes decrease with tree height? g ---A mechanical view
advertisement

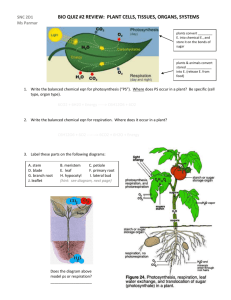
Why the mesophyll cell sizes decrease with tree height? g ---A A mechanical view Ming GUO 01/11/2008 Mesophyll cell sizes versus heights Red Scale Bar = 20 μm Mesophyll cell sizes versus heights Mesophyll cell diameter (μm) 30 Parashorea a as o ea cchinensis e ss Terminalia bellirica Dysoxylum cupuliforme Elaeocarpus braceanus Syzygium y yg latilimbum Parthenocissus quinquefolia 25 20 Populus opu us tomentosa to e tosa Populus hopeiensis Fraxinus chinensis Ginkgo biloba Platanus orientalis Wisteria sinensis Lonicera maackii Parthenocissus tricuspidata Buxus bodinieri 15 10 5 0 20 40 Leaf height (m) 60 80 Summary on observations • Our microscopic observations of mesophyll cells reveal that the cell sizes are remarkably reduced with increasing heights of f th the lleaves. s • The reduction rates depend strongly upon the growth regions. • My previous explanation was based on a famous plant growth model. Why the mesophyll cell sizes d decrease with h tree height, h h from the view of mechanics? 3. Evaporation into air (transpiration) 22. Transport in xylem vessels Plant Physiology, 3rd ed. (2005) 1. Absorb water from soil by roots Mesophyll cells – The Engines Symplasm water 10~40 nm pores on outer surface generate large negative pressure ~MPa How Tall Can Trees Grow? Koch, G. W., Sillett, S. C., Jennings, G. M. & Davis, S. D. The limits to tree height. height Nature 428, 851-854 (2004) Relationship Between Xylem P Pressure and dT Tree Height H i h Predawn Midday Hydrostatic gradient before dawn is equal to the gradient due to gravity. At midday, 2/3 of the xylem l pressure d due tto gravity. Guess negative water pressure is the reason. • An important process in tree’s life is the continuous water transport to tree leaves leaves, which is mainly driven by the negative pressure inside the leaf mesophyll cells cells, generated by transpiration. • However, H th effects the ff t off these th negative ti pressures on the mesophyll cells are mostly tl unknown. k Focus on cells under transpiration! Negative Pressures ¾ Transpiration on nanoscale wall-pores generate negative pressure in apoplast water water. ¾ Xylem negative pressures become more negative with increasing height. ¾ What’s the effects of negative pressure to the evolution and structure of mesophyll cells? 2R Negative Pressure Negative apoplast water pressure Straw Collapse Analogy When drinking furiously through a straw, the straw may suddenly collapse into flat flat, due to the negative pressure inside. inside Straw Collapse Analogy F cylindrical For li d i l thi thin shell: h ll 2 Et 3 Pcr = 3 D 1− v2 ( ) 2 Et 3 so, Dcr = 3 (1 −ν 2 ) P Timoshenko, Theory of elastic stability Elastic Instability Mechanism f large for l cells ll sever transpiration p cylindrical shell model: 3 2 Et D < Dcr = 3 2 (1 −ν ) P Mesophyll cell sizes versus heights Red Scale Bar = 20 μm Strength Failure Mechanism f smallll cells for ll Assume isotropic elastic material σr | D r = −t 2 =P σ r |r =D / 2 = 0 P(D − 2t ) PD (D − 2t ) + σr = − 2 2 2 2 2 D − (D − 2t ) 4 D − (D − 2t ) r 2 2 ( 2 ) P(D − 2t ) PD (D − 2t ) − σφ = − 2 2 2 2 D − (D − 2t ) 4 D − (D − 2t ) r 2 2 2 ( 2 ) Strength Failure Mechanism f smallll cells for ll Max stresses: σ r |r = a = P D + (D − 2t ) σ φ |r = a = − 2 P 2 D − (D − 2t ) 2 2 Strength criteria: | σ r (r = a ) |= P < σ s + (= tensile strength ) D 2 + (D − 2t ) | σ φ (r = a ) |= 2 P < σ s − (= compressiv p e strength g ) 2 D − (D − 2t ) 2 Strength Failure Mechanism f smallll cells for ll So 2 ⎡ σ ⎤ σ ⎛ ⎞ D < Dcr ~ ⎢1 + s − + ⎜ s − ⎟ − 1⎥t P P ⎠ ⎥ ⎢ ⎝ ⎣ ⎦ Detailed parameters parameters… Plow = P0 + ( n + 1) ρ gH extra pressure flow resistance index E = 130 MPa; υ = 0.3; t = 1.5 μm σ s − = 2.3 MPa for rainforest trees σ s − = 3.5 MPa dry-temperate trees Curve fitting results: n = 0.5 for rainforest zone trees n = 4.6 4 6 ffor d dry-temperate zone trees Model Estimates elastic instability mechanism, BLACK lines material failure mechanism , RED lines In both h mechanisms, h leaf l cells ll should h l decrease their h sizes to prevent structure and material collapse, with increasing height.