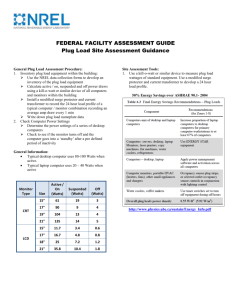
Power Consumption (Watts)
advertisement

Session 10: Energy Efficiency in Information Technology Equipment Agenda • • • • • • • What is Green IT? Defining End User Devices Power Consumption Power Management Mobile Computing Printing Where to next? What is Green IT? “Green IT is the conscious implementation of technologies, techniques and policies designed to reduce the carbon footprint of the IT function within the organisation … … and the use of IT to reduce the carbon footprint of the whole organisation” End User Efficiencies • Desktop computing • Mobile computing • Printing Power Consumption • PCs, Displays, Printers and other components • How is power measured? • How much does it cost? • What is the annual cost? Power Consumption Example • Assumptions: – Energy is charged at 20c per kWh – 1 PC uses 100W • What is the cost for 100 PCs for one 8 hour day? • What is the cost per year? Power Consumption Example Solution • Energy per PC per hour: 100W x 1hr = 100Wh = 0.1kWh • Cost per PC per hour: 0.1kWh x 20c = 2c • Cost per PC per 8 hour day: 2c x 8hr = 16c • Cost for 100 PC per day: 100 x 16c = $16.00 • Cost for 100 PC per year: $16 x 365 = $5840 Component Power System Unit Type (without monitor) Power Consumption (Watts) Conventional Desktop PC – no power management 110W Conventional Desktop PC – power management 90W “Green PC” 80W Laptop PC 60W Notebook PC 40W Thin Client 15W Monitor type Power Consumption (Watts) Conventional CRT monitor – 19 inch 140W Conventional CRT monitor - 17 inch 80W LCD Monitor – 19 inch 50W LCD Monitor – 17 inch 30W OLED Monitor 10W Figures at as 2008 Activity 1 • Measure power consumption of desktop appliances Power Management • All modern operating systems have power management facilities built in • Decreases power consumption by more than 50% • Reduces the need for cooling Should you Turn Them Off? • Turning PCs off will reduce the power consumption but will reduce productivity • Use power management during work hours and turn off at other times. • Use Server Policies to force shutdown after hours ComputersOff.org • Did you know that putting your PC to “sleep” or turning it off when you’re not using it, can save you up to $80 on your power bill and reduce your computer’s carbon emissions by up to 100kg over 12 months. That’s the same amount of C02 you emit by flying from Sydney to Canberra! (www.computersoff.org) Mobile Computing • Laptops, Netbooks and PDAs • Use less power than desktops but can still have savings • Use power adapter when possible • Turn off features when not in use • Use wired network if possible • Enables teleworking, reduces travel • Shorter life span means more disposal Printers and Print Management • Does duplex printing help? • Don’t print as much and use print settings to reduce output • Use fewer printers with better power management. • Use billing to change behaviour Activity 2 • Make calculations using EnergyStar website • Make suggestions for reducing power consumption – this must be submitted for assessment. Other ways of reducing the Carbon Footprint • Procurement • Reuse, refurbish, redeploy and recycle • Ethical Disposal • Video – Toxic Trade http://www.pbs.org/frontlineworld/stories/ghana804/video/video_index.html Other energy efficiency/ IT topics • Datacentre power consumption – Virtualisation – Cooling – Cloud Computing • IT as an enabler for reducing enterprise carbon footprint – Carbon Emissions Reporting – Teleworking Useful websites • http://www.energystar.gov.au/products/co mputers.html • http://michaelbluejay.com/electricity/compu ters.html • http://www.computersoff.org/