l10_mega_cities
advertisement

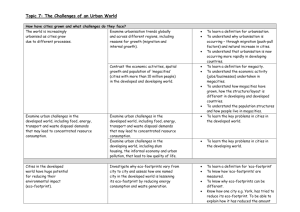
Session 10 Defining and Investigating World Cities Session 11 Defining and Investigating World Cities Sessions 10 & 11: WORLD CITIES UNIT 1: GOING GLOBAL Learning Objectives 1. To define a world city, million city and mega city 2. To describe the causes (push and pull) of rural-urban migration 3. Describe and explain the global pattern of megacities, including regional variations in growth rates Starter: Obj 1: To define a world city, million city and mega city Sort the cards to match definitions and examples • World cities = A city able to have an effect on global affairs through it’s socio-economic resources and importance in global networks • Million cities = Metropolitan areas with a population in excess of 1 million inhabitants • Mega cities = Metropolitan areas with a population in excess of 10 million inhabitants List of largest cities: http://www.mongabay.com/igapo/cities.htm Identify which category the following belong to and be ready to explain your answer Delhi Brussels Newcastle Upon Tyne Identify which category the following belong to and be ready to explain your answer • All of these cities are million cities • Delhi is the only ‘mega city’ (16,700,000) and has the fastest growth rate of any megacity in the world (4.6% per year!) • Brussels is the ‘Capital city’ of the European Union... Just over 1 million but an important world city. • Newcastle Upon Tyne is the smallest million city in the UK, with a population of 1,100,000 Urbanisation –p114-15 blue book Obj 2: To describe the causes (push and pull) of rural-urban migration • What is urbanisation? • What causes urbanisation? (create a definition plus a table of push and pull factors) • What is urbanisation? Urbanisation is the increase in the proportion of people living in towns and cities. • What causes urbanisation? Urbanisation occurs because people move from rural areas (countryside) to urban areas (towns and cities). This usually occurs when a country is still developing. The UN predicts that by 2030 60% of the world's population will live in urban environments. Rural push factors Urban pull factors •Lack of resources to support the growing population eg. Wood for fuel and shelter •Lack of employment opportunities (reliance on agriculture) •Lack of new opportunities •Poor infrastructure eg. Poor roads, plumbing, telephone connections •Lack of local healthcare/education •Mechanisation of agriculture may mean less need for people on the land •Opportunities for employment (within formal and informal sectors) •Job opportunities in TNCs •Perceived quality of lifestyle •Provision of services and infrastructure •Modern Housing •The lure of a global hub •Improved transport makes travel to urban areas easier •Opportunities presented by development schemes •Relaxation of migration laws Obj 2: To describe the causes (push and pull) of rural-urban migration • Work in pairs • One partner read through and complete the comparison worksheet for Los Angeles (pages 110-115 Digby et al) • One partner read through and complete the comparison worksheet for Mumbai (pages -121 Digby et al/p116-117 edexcel text book) • Together agree three similarities and three differences between the process of urbanisation in Los Angeles and Mumbai Obj 3: Describe and explain the global pattern of megacities, including regional variations in growth rates • Urbanisation is closely linked to development – areas currently experiencing the fastest urbanisation are NICs and LEDCs Watch the following films. Urbanisation lagos Welcome to Lagos As you watch take notes on: Key facts and background information Challenges and problems faced (video 1) Opportunities provided by urban living (video 2) Describe and explain the global pattern of megacities, including regional variations in growth rates Urbanisation in the late 20th century A more urban world – but how has this happened? Urbanisation in the late 20th century • The growth of an urban population BBC LINK • Europe/N.America are the most urbanised regions 50’s/60’s • Rapid growth in S.America and Africa • S.America continues to rapidly urbanise 70’s/80’s • Asia begins to urbanise at an increasing rate 90’s/00’s / beyond • Urban pop in MEDCs stabilises • Highest urban growth rates found in Asia and Africa • Highest % increases in Africa...but volume in Asia much higher Mega City Exam practice - resources exam questions on mega cities – you have 7 minutes to complete a) What is a megacity? (1) b) Using the photographs and your own knowledge, complete the table to contrast the characteristics of the two megacities shown Self Mark *10 Study Figure 10. (a) Suggest why there is an urgent need to improve residential slums such as Dharavi. (10) (b) Explain why many megacities are currently experiencing rapid rates of growth. (15) Answer part B You have 15-20 minutes! Homework 1. Complete the 2 exam questions under timed conditions 2. Start revising for the mock exam Optional hmk: 1. Watch Andrew Marr’s Mega Cities1: Living in the City – Available on the LRC CLICK VIEW Make notes under the titles ‘winners’ and ‘losers’, making notes on mini case-studies to add to your understanding of mega-cities. 2. Watch the Lagos clips and make notes as per the slide instructions