Female Reproductive System
Today you’ll learn about the organs
that make up the female
reproductive system and how they
function. During puberty, females
become capable of becoming
pregnant and having a baby. Each of
the organs you’ll learn about today
plays a role.
The external female reproductive
organs—the labia majora, labia
minora, clitoris, urinary opening,
and vaginal opening—are
collectively referred to as the vulva.
Female Reproductive Organs - External
The mons pubis is the fatty
tissue covering the pubic bone.
Female Reproductive Organs - External
The labia majora (outer lips) and the
labia minora (inner lips) are folds of
skin that surround and protect the
other external reproductive parts:
the clitoris, vaginal opening, and
urethral opening.
Female Reproductive Organs - External
The clitoris is about the size of a pea
and is full of sensitive nerve endings.
Its purpose is to provide sexual
pleasure.
Female Reproductive Organs - External
Below the clitoris is the urinary
opening. Urine leaves the body
through this opening.
Female Reproductive Organs - External
Below the urethral opening is the
opening to the vagina—a muscular
tunnel that is about 4 inches long.
The vagina connects the female’s
external and internal sex organs.
This is where menstrual fluid leaves
the body. It’s where the male’s
penis is inserted during intercourse.
It’s also the passage through which a
baby is born, so it’s sometimes
called “the birth canal”.
Female Reproductive Organs - External
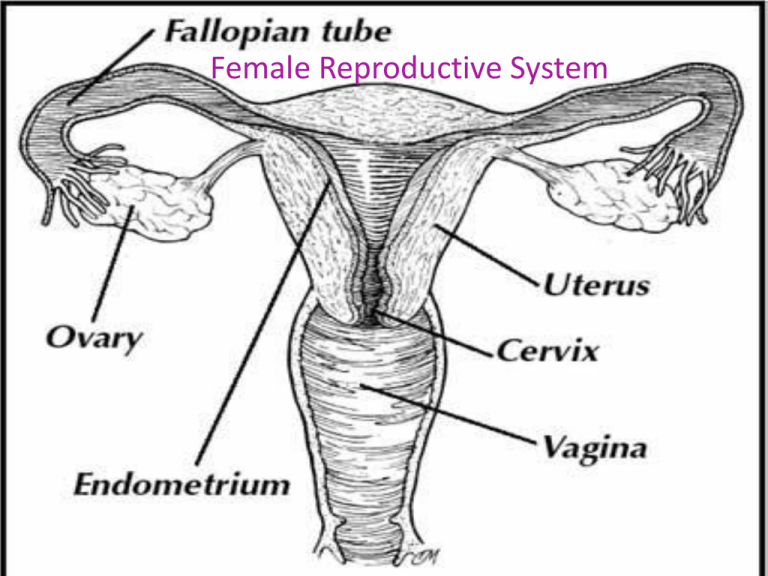
The internal female reproductive
organs include the vagina, uterus,
fallopian tubes and ovaries.
The uterus is a pear-shaped organ,
about the size of a fist. It is one of
the strongest muscles in the body.
It’s where a fertilized egg grows and
develops while a woman is
pregnant.
Female Reproductive Organs - Internal
The ovaries are almond-sized organs
that make female hormones and
hold the female’s eggs. At birth, the
ovaries contain more that 300,000
egg cells.
Female Reproductive Organs - Internal
The fallopian tubes come out of
each side of the uterus. An egg
travels from an ovary through a
fallopian tube into the uterus.
Fertilization happens when a male
sperm enters the female egg while it
is in the fallopian tube.
Female Reproductive Organs - Internal
The cervix is the end of the uterus
that opens into the vagina. During
pregnancy, it stays tightly closed to
help protect the fetus.
Female Reproductive Organs - Internal
Turn to “Female Reproductive
Organs” on page 6.
Take a card that will either have a
term, or a definition on it. Find right
term or definition to match your
card. Sit in a desk next to that
person. When everyone is done we
will go through the worksheet
together based on your definitions.