river valley civilizations
advertisement

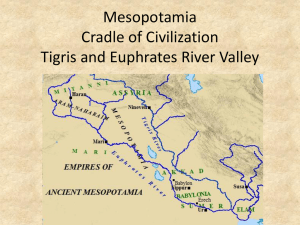
1. What major rivers are seen on this map? 2. Why is this region called “the Fertile Crescent”? 3. What civilizations were located here? RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS MESOPOTAMIA Essential Question: What were the important characteristics of the civilizations in Mesopotamia? Warm-Up Question: Why was the Neolithic Revolution such a big deal? Which of the 5 characteristics of civilizations do you think is most important? RIVER VALLEY CIVILIZATIONS The discovery of farming during the Neolithic Revolution allowed nomadic people to settle into villages and towns; these eventually became civilizations Ancient Egypt The world’s first civilizations all began in river valleys Indus Valley The first civilization began in an area known as Mesopotamia China The Tigris and Euphrates Rivers flooded once per year, leaving behind fertile soil ideal for farming (a perfect place to start a civilization) Mesopotamia means “land between the rivers” and is often called the “Fertile Crescent” or referred to as the “Cradle of Civilization” The first civilization that developed in the “Fertile Crescent” of Mesopotamia was the kingdom of Sumer Surrounding deserts and the lack of natural barriers attracted outsiders to Mesopotamia and made the Sumerians vulnerable to attack; this led to other kingdoms rising in Mesopotamia LASTING CONTRIBUTIONS ADVANCED CITIES: Sumerian city-states were protected by high walls At the city center was a temple called a ziggurat LASTING CONTRIBUTIONS SPECIALIZED WORKERS: At the top of society were priests, and then kings In the middle were skilled workers, like merchants At the bottom, were common farmers and slaves LASTING CONTRIBUTIONS (COMPLEX INSTITUTIONS) RELIGION: Sumerians and Babylonians were polytheistic (many gods) LASTING CONTRIBUTIONS (COMPLEX INSTITUTIONS) RELIGION: The Hebrews in Palestine were the first monotheistic (single god) faith in history (Judaism) The holy book of Judaism is the Torah; God gave Moses the Ten Commandments LASTING CONTRIBUTIONS GOVERNMENT: Babylonian King Hammurabi created the first legal code Hammurabi’s Code had 282 laws based on justice and retaliation (for example: “an eye for an eye”) The code had different LASTING CONTRIBUTIONS LASTING CONTRIBUTIONS WRITING: Sumerians made the world’s first writing called cuneiform WRITING: –Phoenicians simplified cuneiform to a 22 letter alphabet –Phoenician merchants spread the alphabet throughout the Mediterranean world –The alphabet LASTING CONTRIBUTIONS TECHNOLOGY: Sumerian inventions include the wheel, sail, plow, and bronze metalwork After thousands of years of civilization in river valleys, the world’s first empires appeared River valley civilizations were complex societies with advanced technologies, cities, workers, writing, and institutions (religions and governments) Like river valley civilizations, empires were advanced societies with well-organized, centralized governments The difference is that empires conquer and rule over a variety of formerly independent people “EMPIRE” defined: a group of several different nations or people united and ruled over by a monarch (like an emperor or king) The nations that are ruled over obey and serve the mother country of the empire In the first ancient empire we learn about, the mother country of the empire was Persia Major Empires Han Dynasty Persian Empire in China Mauryan and Gupta Empires in India Mesopotamia: River Valley to Empire The fertile soil and lack of natural boundaries (like mountains) in Mesopotamia led to the Mesopotamian civilizations being the target of frequent invasions and conquests One of the most important ancient empires was Persia (present-day Iran) The Persians grew into a powerful empire under Kings Cyrus and Darius With a powerful army, the Persians conquered Mesopotamia, Egypt, and India The “10,000 Immortals”: Persia’s elite fighting force Persia’s religion was Zoroastrianism (based on the teachings of the prophet Zoroaster) This religion viewed life as a struggle between good and evil; the Persians believed in Heaven and Hell as consequences for how they lived their lives Zoroastrianism influenced the views of the afterlife in Judaism, Christianity, and Islam How did the Persians control such The Persian Empire at its Height a massive empire? PERSIA’S SYSTEM OF CONTROL Persia controlled their lands in a variety of ways Persian kings were tolerant; they allowed conquered people to keep their languages and religions This kept the conquered people content and less likely to rebel PERSIA’S SYSTEM OF CONTROL Rather than destroying or looting conquered cities, King Cyrus would show respect for local customs As the mother country of the empire, the Persians were definitely in charge However, life was tolerable under Persian rule, so this made most conquered people content THE PERSIAN EMPIRE AT THE HEIGHT OF ITS POWER King Darius divided the empire into twenty provinces, each one was ruled by a satrap (local governor) Satraps served PERSIA’S SYSTEM OF CONTROL as the “eyes and ears” of the Persian kings in their respective provinces They collected taxes from the people of the provinces and informed the king of any uprisings PERSIA’S ORGANIZED EMPIRE The Persians built a network of roads in order to collect taxes, improve communication, and facilitate trade throughout their empire PERSIA’S ORGANIZED EMPIRE The Persians used metal coins with standardized values to help promote trade