Persian Empire
advertisement

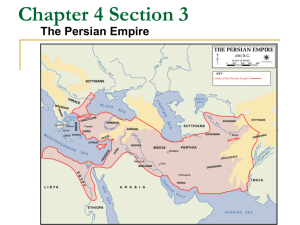
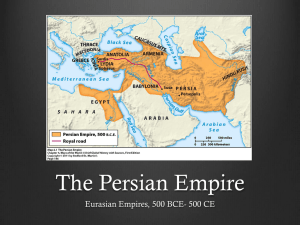
Persian Empire The World’s First Superpower Objectives • Students will discover who shaped the growth and organization of the Persian Empire. •Students will explore the main teachings of Zoroastrianism. •Students will identify the most significant cultural achievements of the Persians •Students will discover the connections between ancient Persia and Modern Iran Theme 1: Government Persia under the Medes Cyrus the Great • Both Indo-European tribes • Medes conquered Persians • Defeated Medes in 559 BC • Expanded Persian Empire • Persians allowed to keep their own leaders as long as they did not rebel • Freed Jews in Babylon • Respected by those he conquered Darius I • Crushed rebellion after death of Cyrus’s son • Strengthened army, empire • Tried to invade Greece, turned back at Marathon. • Ceremony and ritual • Created satraps to help govern Persia in Decline • Rule of Darius high point of Persian culture • Son, Xerxes, failed to conquer Greece • Last strong ruler of Persia • Following leaders weak and ineffective Cyrus the Great Darius I Xerxes Cyrus Cylinder has also been claimed to be an early "human rights charter" http://robotchicken.wikia.com/ wiki/1776 Persian Military • Military was the key in building the worlds first superpower • Used Cavalry and Chariots – Chariots were unique because the were pulled by four horses – Also carried archers who pelted foes with arrows from a distance • Supported by highly trained troops called the Immortals Theme 2: Religion • Zoroastrianism – Based on the teachings of Zoroaster • God = Ahura Mazda – God was the source of everything good, true and pure in the world. • Evil spirit = Ahriman – Spirits were locked in eternal struggle against each other – Dualism • First religion to believe that the world is controlled by two opposing forces, good and evil • Believed that good would eventually win and rid the world of evil – Polytheistic with an emphasis on Ahura Mazda – Avesta, the sacred text of Zoroastrianism Theme 3: Writing • Branch of Indo European Languages • Old Persian Cuneiform • Written and spoken language Theme 4: Math and Science • The Royal Road, the world’s first long highway. It stretched more than 1,500 miles and linked major cities • Roads built for faster communication and the moving of military forces Theme 5: Art • The Persians were also widely admired for their art. They crafted delicate drinking vessels out of gold set with precious gems. – Many of these golden objects are shaped like animals, such as lions and bulls. Animals were a common subject in Persian art. • Many archaeologists consider Persepolis (capital) the greatest example of Persian architecture. • Designed as a ceremonial city by Darius I, the entire city of Persepolis was a monument to Persia’s glory. • At the center of the city was a high-ceilinged audience hall unlike anything else in the Ancient Near East. http://ngm.nationalgeographic.com/2008/08/iran-archaeology/iran-photography Audience Hall http://ngm.nationalgeographic.com/2008/08/iran-archaeology/iran-photography Theme 6: Trade • Coin money issued • Encouraged trade by building roads throughout the Persian Empire • As a result of this increased trade, the empire grew richer.