Ionising radiation Task 2 pupil
advertisement

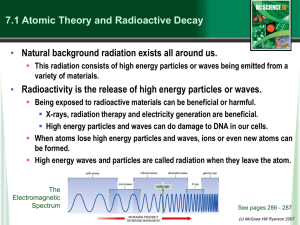
Ionising radiation BTEC Assignment 1 Task 2) and 2b) TITLE: Ionising Radiation Assignment Task 2a/b Objectives (We are learning that): • • • Describe the different types of ionising radiation. (PASS) Describe the problems associated with the use of radioactive isotopes. (PASS) Compare the benefits and drawbacks of using radioactive isotopes in the home or workplace. (MERIT) Outcomes: You should be able to... •Review what the definition of an isotope is •State the 3 types of ionising radiation and what the word ‘ionising’ means by drawing a diagram on paper or ICT to explain what harm it has on the body. (use references in all research) •Create a collage on the penetrating power of the 3 types of ionising radiation using slide 7 •Draw a diagram to compare the dangers inside and outside the body of radiation •Complete a summary table of the problems and dangers of isotopes KEY WORDS: Radiation Alpha Beta Gamma Atom Nuclear model Half life Isotope Task 2: The good and bad of using isotopes Having told the year 11 learners about ionising radiation, you should now tell them about using these exciting but dangerous radioactive isotopes. 2a) To prepare for the lesson you need to research the effect that ionising radiation from radioactive isotopes has on living cells. Use your research to write a description of the problems and dangers linked to use of radioactive isotopes. (PASS) Useful links • http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/sc ience/edexcel/electromagnetic_spectrum/elec tromagneticspectrumrev5.shtml • Substances which constantly give out radiation are said to be R_________. • It involves a change in the structure of the n_____ of the radioactive atom which releases one of the 3 types of radiation: • We call them R________________ • Alpha (α) • Beta (β) • Gamma(γ) Alpha, Beta and Gamma are known as I………….. Radiation. ION Radiation alpha/beta/gamma Knocked off electron •When RADIATION collides with NEUTRAL ATOMS or MOLECULES they can become charged due to electrons being ‘knocked off’ or ‘added’ to their structure. •This changes their structure leaving them as I……… or (C……………. PARTICLES). Ionising radiation What happens if radiation hits a living cell? Radiation can ionise cells which causes c________ d______. If the exposure is h____, it can kill the cell. If the exposure is l_____ it can cause cancer. The higher the exposure, ..... Ionising radiation can be used to kill cancer cells. The penetration power of the three types of radiation (PASS) Thin plastic Skin or paper stops ALPHA Thin aluminium stops BETA Thick lead reduces GAMMA Radiation outside the body Radiation inside the body Using your knowledge, fill in the table below: Alpha Penetrating power Range of radiation Most dangerous outside of body Most dangerous inside of body Beta Gamma Quick Questions: Which type of radiation is….. 1. The most penetrating? 2. The least penetrating? 3. Least dangerous outside the body? 4. Most dangerous inside the body? 5. High energy electrons? 6. Has a negative charge? 7. Is weakly ionising? 8. Has zero charge and zero mass? 9. Only reduced in intensity by lead and concrete? 10. The most ionising radiation? Task 2b) • In order to show the variety of uses of radioactive isotopes you need to draw a table listing some uses in devices at home and in the workplace. For each isotope listed in your table, include the advantages and disadvantages of using them. (MERIT)