What is Science
advertisement

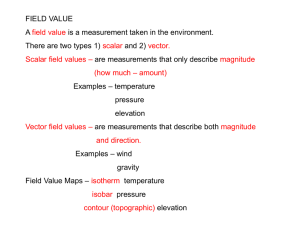
Chapter 1 A framework of lines that helps to transfer points on Earth’s surface onto a flat map. map projection The size and shape of landmasses become more distorted toward the north and south poles on this type of projection. Mercator projection One half of the sphere that makes up Earth’s surface. hemisphere A list of symbols used on a map and their meanings. key A spherical model of Earth’s entire surface. globe This is how many degrees you travel if you circle the globe completely and return to the spot form where you departed. 360⁰ The distance in degrees north or south of the equator. latitude This is the latitude of the North Pole. 90⁰ These are the units used by scientists to locate positions on Earth’s surface. degrees The distance in degrees east or west of the prime meridian. longitude Used to relate distance on a map or globe to distance on Earth’s surface. scale A flat model of all or part of Earth’s surface as seen from above. map The line that makes a half circle form the North Pole to the South Pole and that passes through Greenwich, England. prime meridian An imaginary line that circles Earth halfway between the North and South poles. equator On a map, a picture used by mapmakers to stand for features on Earth’s surface. symbol One bit of a digitized image, often appearing as a small square or dot. pixel A satellite-based system that can precisely determine latitude and longitude for points on Earth’s surface. Global Positioning System (GPS) This is how many satellites above the horizon there must be at any given time for the GPS to work. At least 3 The difference in elevation from one contour line to the next. contour interval A system of computer hardware and software used to produce interactive maps. Geographic Information System A photograph taken by cameras mounted in airplanes. aerial photograph Converting information to numbers for use by a computer. digitizing This is why computer mapmakers digitize map data. so they can display the data on a computer screen A line on a topographic map that connects points of equal elevation. contour line A line on a topographic map that connects points of equal elevation (the further apart the contour lines are, the easier it is to walk up the slope). contour line On a topographic map, a heavier contour line that is labeled with elevation of that contour line. index contour A picture of the land surface based on computer data collected from satellites. satellite image A map that shows the surface features of an area. topographic map The process of gathering data for a map by using instruments and the principles of geometry to determine distance and elevations. surveying The difference in elevation between the highest and lowest parts of an area. relief A landform made up of flat or gently rolling land with low relief. plain This is the vast, flat or gently rolling grassland in the interior of North America. Great Plains A group of mountains that are closely related in shape, structure, and age. mountain range A feature of topography formed by the processes that shape Earth’s surface (ex. hill, valley). landform A landform with high elevation and high relief (ex. Rocky Mountains). mountain A large area of land where the topography is made up mainly of one type of landform. landform region The shape of the land determined by elevation, relief, and landforms. topography A landform that has high elevation and a more or less level surface. plateau Height above sea level and also one of the major differences between a coastal plain and an interior plain. elevation This is shown on a topographic map by hachured contour lines. depression