12-nervoussystemintro - Alexmac
advertisement

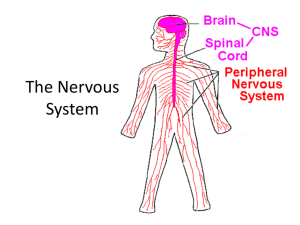
Do Now http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=i-NgGKSNiNw • How do you communicate messages to friends? • What are the purposes of these messages? What are the functions of the nervous system? The main functions of nervous system are communication and coordination of body activities. This is done by transmitting signals between the brain and the rest of body. Q: What are the functions of the nervous system? 1. Collect information about the body’s environment – Internally and externally 2. Process the information 3. Create a response – The brain or spinal cord creates and sends a response to the body There are two functioning parts of the nervous system: 1. Central Nervous System – Brain and spinal cord – Processes information and creates response 2. Peripheral Nervous System – Nerves that connect the body to the central nervous system. They carry signals between the central nervous system and body. Central vs. Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Consists of different types of cells; • Nerves that carry information from the sensory organs, ( skin, ear, eye, tongue, nose), • Nerves that control the voluntary muscles, • Nerves that regulate involuntary functions such as breathing, digestion, and heartbeat. • Nerves are made of bundles of neurons , each surrounded by connective tissue. Central Nervous System Protection • Skull protects the brain. • Spine protects the spinal cord. • Cerebrospinal fluid surrounds and cushions the brain and the spinal cord. It transports chemicals and removes waste from the central nervous system. Which diagram is showing the nervous system? Nerve tissue • Is found in the brain, the spinal cord and in the nerves. • It is mainly made up of neurons. How is the information collected by the nervous system carried through the body? • Messages carrying information through the nervous system are ELECTRICAL SIGNALS called IMPULSES • NEURONS are cells that carry and pass along these signals – Neurons are the main cells of the nervous system “The functional units of the nervous system” Structure of Neuron • Cell Body – contains nucleus and much of cytoplasm • Dendrites – receive impulses (messages) from other neurons • Axon – long fiber carrying impulses away to the next neuron Quick Check… • What are each letters? • Are there more dendrites or axons in a neuron? How do electrical cords ensure the electricity stays within the wire? Lets make sure the message doesn’t get lost… • The axon is surrounded by a MYELIN SHEATH – Keeps electric signal within the axon – Causes the signal to move faster Repair of Neurons • Injured neurons in the central nervous system don’t regenerate easily. • Some neurons in peripheral nervous system can regrow and repair a small gap. Start an impulse • Stimuli cause electric signals – A stimulus is a detectable change in the environment. • Impulses begin when neurons Are stimulated by another neuron or by the environment. Sensory Receptors • Sensory receptors are structures in the skin and other tissues that detect changes in the internal or external environment. These receptors consist of specialized neuron endings or specialized cells in close contact with neurons that convert the energy of the stimulus (sound, color, odor, etc.) to electrical signals within the nervous system. Sensory receptors, together with other cells, compose the major sense organs, including eyes, ears, nose, and taste buds. Information from different sensory receptors go to specific parts of the brain. • Read 3.10 • Bionic Arm, Diseases and disorders • H.W. page 107 #1-7 How are messages passed between neurons and other cells? • The space between two neurons is called a SYNAPSE Moving the signal between cells • Once the signal reaches the end of the axon: 1. NEUROTRANSMITTERS are released into the synapse 2. The neurotransmitters travel across synapse and bind to CELL RECEPTORS (shape!!) on the next neuron 3. The target cell takes message from receptors and continues moving the signal Regents Review • The diagram represents the functional unit of a nervous system. Which structure secretes a neurotransmitter? Which structure contains cell receptors that bind neurotransmitters? • structure A • structure B • structure C • structure D Synapse and Neurotransmitters 1http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FR4S1BqdFG4&safety_mode=true&persist_safety_mode= 1&safe=active 2http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FR4S1BqdFG4&safety_mode=true&persist_safety_mode= 1&safe=active 3http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=endscreen&v=qMsWtP3VS3Q&NR=1