review for 8th grade quarterly - Clarence Central School District
advertisement

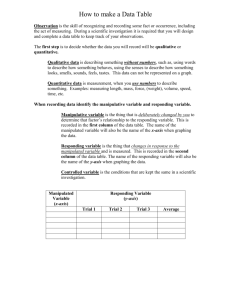
REVIEW FOR 8TH GRADE QUARTERLY DR. GERARD MAKIN CLARENCE MIDDLE SCHOOL CHEMICAL CHANGES • A chemical change has occurred when: 1. There is a color change (rust) 2. A gas is released (baking soda and vinegar) 3. When a precipitate is formed. (vinegar in milk forms curds that fall out of solution) PHYSICAL CHANGE • A PHYSICAL CHANGE IS WHEN A SUBSTANCE CHANGES SHAPE OR STATE WITHOUT CHANGING ITS CHEMCAI PROPERTIES. 1. CUTTING WOOD 2. FREEZING OR BOILING WATER 3. CUTTING HAIR MEASUREMENT • The measurement of a liquid or the amount of space and object takes up is volume measured in liters, milliliters(cc,cm3). • The distance between objects or places is measured in meters or kilometers. • Density is how much matter occupies a specific volume in g/cm3 (how tightly packed the particles are) • The mass of an object is the quantity of matter in an object measured in grams and kilograms(same all over the universe not based on gravity) DENSITY OF LIQUIDS • Liquids of different density will form layers when occupying the same container. DENSITY OF SOLIDS • All objects densities are compared to water which is 1.0 g/cm3 • If an object is less dense than water it will float at some level within that water depending on how close to or far from 1.0 g.cm3 it is. • Objects whose density is greater than 1.0g/cm3 will sink in water. DENSITY OF AN IRREGULAR OBJECT WHICH WILL FLOAT OR SINK PHASE CHANGES • When a phase change is occurring the temperature remains constant. WATER CYCLE • Water evaporates to a gas theN condenses to a cloud and as the air gets colder it further condenses into rain or precipitation. LESSON 4.1 INTERPRETING GRAPHS Practice : For the following line graph, answer the questions given. 1) Barry’s pulse rate is taken every 6 hours over 3 days. The graph shows his pulse rate in beats per minute. (a) Write down the first pulse rate shown on the graph. (b) Write down Barry’s highest pulse rate shown during the three days. (c) Work out the difference between his highest and lowest pulse rates shown on 3rd May. • What is the real-world meaning of the graph at right, which shows the relationship between the number of customers getting haircuts each week and the price charged for each haircut? The number of customers depends on the price of the haircut. So the price in dollars is the independent variable and the number of customers is the dependent variable. As the price increases, the number of customers decreases linearly. As you would expect, fewer people are willing to pay a high price; a lower price attracts more customers. The slope indicates the number of customers lost for each dollar increase. The x-intercept represents the haircut price that is too high for anyone. The y-intercept indicates the number of customers when haircuts are free. EXAMPLE Students at Central High School are complaining that the juice vending machine is frequently empty. Several student council members decide to study this problem. They record the number of cans in the machine at various times during a typical school day and make a graph. EXAMPLE a. Based on the graph, at what times is juice consumed most rapidly? b. When is the machine refilled? How can you tell? c. When is the machine empty? How can you tell? d. What do you think the student council will recommend to solve the problem? SOLUTIONS • Although the student council members in the example are interested in solving a problem related to juice consumption, they could also use the graph to answer many other questions about Central High School: • • • • When do students arrive at school? What time do classes begin? When is lunch? When do classes let out for the day? PART 2 • This graph tells a story. It could be a story about a lake, a bathtub, or whatever you imagine. Spend some time with your group discussing the information contained in the graph. Write a story that conveys all of this information, including when and how the rates of change increase or decrease. IDENTIFYING VARIABLES 3 KINDS OF VARIABLES • Manipulated Variable – something that is changed by the scientist • What is tested • What is manipulated 3 KINDS OF VARIABLES • Responding Variable – something that might be affected by the change in the manipulated variable • What is observed • What is measured • The data collected during the investigation 3 KINDS OF VARIABLES • Controlled Variable – a variable that is not changed • Also called constants • Allow for a “fair test” Students of different ages were given the same jigsaw puzzle to put together. They were timed to see how long it took to finish the puzzle. Identify the variables in this investigation. WHAT WAS THE MANIPULATED VARIABLE? •Ages of the students • Different ages were tested by the scientist WHAT WAS THE RESPONDING VARIABLE? •The time it took to put the puzzle together • The time was observed and measured by the scientist WHAT WAS A CONTROLLED VARIABLE? •Same puzzle • All of the participants were tested with the same puzzle. • It would not have been a fair test if some had an easy 30 piece puzzle and some had a harder 500 piece puzzle. ANOTHER EXAMPLE: AN INVESTIGATION WAS DONE WITH AN ELECTROMAGNETIC SYSTEM MADE FROM A BATTERY AND WIRE WRAPPED AROUND A NAIL. DIFFERENT SIZES OF NAILS WERE USED. THE NUMBER OF PAPER CLIPS THE ELECTROMAGNET COULD PICK UP WAS MEASURED. What are the variables in this investigation? MANIPULATED VARIABLE: •Sizes of nails • These were changed by the scientist RESPONDING VARIABLE: •Number of paper clips picked up • The number of paper clips observed and counted (measured) CONTROLLED VARIABLES: •Battery, wire, type of nail • None of these items were changed ONE MORE: THE HIGHER THE TEMPERATURE OF WATER, THE FASTER AN EGG WILL BOIL. What are the variables in this investigation? The variables • Manipulated variable – temperature of water • Responding variable – time to cook an egg • Controlled variable – type of egg LAST ONE: THE TEMPERATURE OF WATER WAS MEASURED AT DIFFERENT DEPTHS OF A POND. What are the variables in this investigation? The variables • Manipulated variable – depth of the water • Responding variable – temperature • Controlled variable – thermometer