pages.ucsd.edu\dmacleod\159\psyc159 color harmony
advertisement

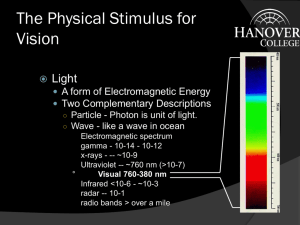
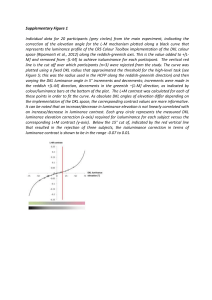
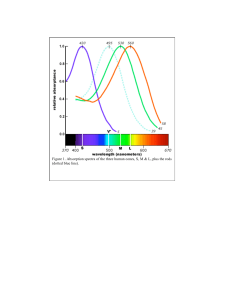
Color Harmony and the Opponent-Process Channel Theory Christina Lewis Psych 159 TRICHROMATIC THEORY Thomas Young and Hermann von Helmholtz, 18’th-19’th century Opponent-Process Theory • 1878 Ewald Hering • Certain color combinations don’t exist (we never see them), such as reddish-green or yellowish-blue • Three receptor types, each with opposing pairs: red green, blue yellow, black white Opponent Neurons • Excitatory response to some wavelengths and inhibitory response to others • Red-Green receptors cannot send information about both colors at the same time • Responses to one color of an opponent channel are antagonistic to those to the other color. **More efficient, given that for the cones, responses to certain wavelengths overlap. Differences are more important. CONES BIPOLAR CELLS GANGLION CELLS PARVOCELLULAR Processes differences between L & M Cones, Red – Green differences MAGNOCELLULAR Processes difference between S cones, blue-yellow differences Intensity of light How it Works • Red-Green Channel: The difference between long-wavelength and middle-wavelength cone signals. • Yellow-Blue Channel: The difference between short wavelength cones and the sum of the other two cones. • *Luminance Channel*: Based on inputs from all the colors. Detects the difference in brightness of color information. ISOLUMINANCE DIFFERENT COLORS - SAME BRIGHTNESS This is a very bad words-on-background color-pair, because there is very little difference between the luminance of the color dark-blue and the luminance of the color black. Youhellohavepsychnoclassproblemthisreadingisonly athereadinggreentestwords. BAD BAD BAD DON’T DO THIS IN YOUR FUTURE POWERPOINTS Implications • Color-opponent channels: • Color is good for SEPARATING OBJECTS • Separating regions • Luminance Channel: • Contrast transmits SHAPE INFORMATION (**edges**) • Fine detail Other Important Properties of Opponent Channels • Luminance > Purely Chromatic Information: • (for many aspects of vision including): • Stereoscopic depth: Cannot detect differences in depth based purely on color channel information Other Important Properties of Color Channels • Motion Perception: • Luminance > Purely Chromatic Information • If gratings of different colors but equal luminance are moving, we detect the speed much slower (or for some humans, completely immobile) as compared to a grating of very large contrast difference (for example a black and white or black and yellow grating). After-Images -Fatigue of one color receptive causes stimulation of its opponent color in the pair