PMI PMBOK GUIDELINES
advertisement

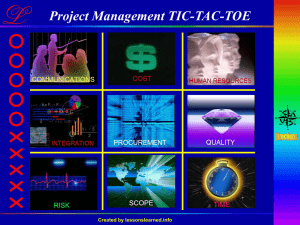
PRESENTED BY TRUST THOMAS EROMOSELE STUDENT NO: 125385 Project Management Body of Knowledge A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide) The PMBOK® is an inclusive term that describes the sum of knowledge within the profession of project management PMBOK® Guide Identifies and describes that subset of the project management body of knowledge that is generally accepted The Definition of a “Project” Program: an exceptionally large, long-range objective that is broken down into a set of projects Project: a specific, finite task to be accomplished Task: set of activities comprising a project A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide) Key Players Stakeholders Anyone actively involved, or have an interest at stake in the project May have influence, responsibility, and authority over the project Project Team Individuals that are performing the project work Typically involves the use of cross-functional teams Project Management Team Project team members that have management responsibilities for the project Key Players Project Manager The individual with overall responsibility for the project Project Sponsor The individual with the authority and resources needed to champion the project effort Typically functions as the linking pin between the project and the parent organization Customer The individual/organization that represents the enduser of the project’s resulting product or service PMI Standards Background 1969 – PMI founded 1983 – PMI Special Report on Ethic, Standards, and Accreditation – the Standards portion was The Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK) 1987 – PMBOK Standard was published 1996 – A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide) [first edition] was published 1999 – PMI accredited as a Standards Development Organization (SDO) by ANSI 2000 – The PMBOK® Guide - 2000 Edition PMBOK (Project Management Body of Knowledge) PMBOK guidelines consist of five process group Initiating Planning Executing Controlling Closing PMBOK PMBOK five process groups PMBOK Process Groups and Knowledge Areas Knowledge Areas The knowledge areas represent the body of knowledge that a project manager must have in order to consistently deliver successful projects that meet a customer’s expectations in terms of scope, time, cost, and quality of the project deliverables 3-10 PMBOK PMBOK nine knowledge areas Project integration management Project scope management Project time management Project cost management Project quality management Project human resource management Project communications management Project risk management Project procurement management Knowledge Areas: Definitions and Component Processes Integration Management:Describes the processes and methods required to identify, define, combine, unify, and coordinate the various processes with the other eight knowledge areas Component Processes:Develop project charter, develop project management plan, direct and manage project execution, monitor and control project work, perform integrated change control, and close project or phase 3-12 Knowledge Areas: Definitions and Component Processes Scope Management:Describes the processes and methods required to ensure that the project delivers exactly what the customer requested and only what the customer requested to create a successful project Component Processes:Collect requirements, define scope,create WBS, verify scope, and control scope 3-13 Knowledge Areas: Definitions and Component Processes Time ManagementDescribes the processes and methods required to create and manage appropriate schedules to complete the project Component Processes:Define activities, sequence activities, estimate activity resources, estimate activity durations, develop schedule,and control schedule 3-14 Knowledge Areas: Definitions and Component Processes Cost ManagementDescribes the processes and methods required to create and manage the project budget Component Processes:Estimate costs, determine budget, and control cost 3-15 Knowledge Areas: Definitions and Component Processes Quality Management Describes the processes and methods required to ensure that the project delivers the stated and implied needs for which it was designed Component Processes:Plan quality, perform quality assurance, and perform quality control 3-16 Knowledge Areas: Definitions and Component Processes Human Resources Management Describes the processes and methods required to eeffectively use the people associated with the project Component Processes:Develop human resources plan, acquire project team, develop project team, and manage project team 3-17 Knowledge Areas: Definitions and Component Processes Communications Management Describes the processes and methods required to create, collect, disseminate, and store information about the project Component Processes:Identify stakeholders, plan communications, distribute information, manage stakeholder expectations, report performance 3-18 Knowledge Areas: Definitions and Component Processes Risk ManagementDescribes the processes and methods required to identify, quantify, and control risks associated with the project Component Processes:Plan risk management, identify risks, perform qualitative risk analysis, perform quantitative risk analysis,plan risk responses, and monitor and control risk 3-19 Knowledge Areas: Definitions and Component Processes Procurement ManagementDescribes the processes and methods required to acquire and manage goods and resources from a source outside the project team Component Processes:Plan procurements, conduct procurements, administer procurements, close procurements 3-20 PMBOK Initiating Processes Initiation (5.1)—committing the organization to begin the next phase of the project. PMBOK Planning Processes Scope Planning —developing a written scope statement as the basis for future project decisions. Scope Definition —subdividing the major project deliverables into smaller, more manageable components. Activity Definition —identifying the specific activities that must be performed to produce the various project deliverables. Activity Sequencing —identifying and documenting interactivity dependencies. Activity Duration Estimating —estimating the number of work periods which will be needed to complete individual activities. Schedule Development —analyzing activity sequences, activity durations, and resource requirements to create the project schedule. PMBOK Planning Processes. cont. Resource Planning —determining what resources (people, equipment, materials) and what quantities of each should be used to perform project activities. Cost Estimating —developing an approximation (estimate) of the costs of the resources needed to complete project activities. Cost Budgeting —allocating the overall cost estimate to individual work items. Project Plan Development —taking the results of other planning processes and putting them into a consistent, coherent document. PMBOK Planning Processes cont. Quality Planning —identifying which quality standards are relevant to the project and determining how to satisfy them. Organizational Planning —identifying, documenting, and assigning project roles, responsibilities, and reporting relationships. Staff Acquisition —getting the human resources needed assigned to and working on the project. Communications Planning —determining the information and communications needs of the stakeholders: who needs what information, when will they need it, and how will it be given to them PMBOK Planning Processes cont. Risk Identification —determining which risks are likely to affect the project and documenting the characteristics of each. Risk Quantification —evaluating risks and risk interactions to assess the range of possible project outcomes. Risk Response Development —defining enhancement steps for opportunities and responses to threats. Procurement Planning —determining what to procure and when. Solicitation Planning —documenting product requirements and identifying potential sources PMBOK Executing Processes PMBOK Executing Processes Project Plan Execution —carrying out the project plan by performing the activities included therein. Scope Verification —formalizing acceptance of the project scope. Quality Assurance —evaluating overall project performance on a regular basis to provide confidence that the project will satisfy the relevant quality standards. Team Development —developing individual and group skills to enhance project performance. PMBOK Executing Processes cont. Information Distribution —making needed information available to project stakeholders in a timely manner. Solicitation —obtaining quotations, bids, offers, or proposals as appropriate. Source Selection —choosing from among potential sellers. Contract Administration —managing the relationship with the seller. PMBOK Controlling Processes PMBOK Controlling Processes Overall Change Control —coordinating changes across the entire project. Scope Change Control —controlling changes to project scope. Schedule Control —controlling changes to the project schedule. Cost Control —controlling changes to the project budget. PMBOK Controlling Processes cont. Quality Control —monitoring specific project results to determine if they comply with relevant quality standards and identifying ways to eliminate causes of unsatisfactory performance. Performance Reporting —collecting and disseminating performance information. This includes status reporting, progress measurement, and forecasting. Risk Response Control —responding to changes in risk over the course of the project. PMBOK Closing Processes PMBOK Closing Processes Administrative Closure —generating, gathering, and disseminating information to formalize phase or project completion. Contract Close-out —completion and settlement of the contract, including resolution of any open items THANK YOU FOR LISTENING!