8C MICROBES AND DISEASE
advertisement

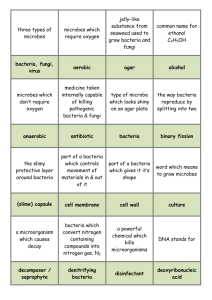
8C MICROBES AND DISEASE MICROBES • What is a microbe? • What are the three types of microbes? Give an example of each. • What do we use microbes to make? Top trumps Micro-organisms The word MICRO means very small. (So you need a Microscope to see it!) http://www.cellsalive.com/howbig.ht m Micro-organism Man! Micro-organisms Micro-organisms Micro- very small Organism- a living thing. So Micro-organisms are very small living things! N.B Viruses are often classed as microorganisms but technically they are NON-Living so call them Microbes instead! Microorganism man Microbe uses carousel • You will be assessed in this activity for AF2 Seven wonders of the microbe world Bread mould experiment • You are going to look at mould growing on bread over 2 weeks. Diseases • What is the scientific word for a microbe that causes disease? • Name an example of a disease caused by a bacteria, virus and fungus? Bacteria The good the bad and the ugly! Bacteria are small living single celled organisms that can come in good (beneficial) forms and bad (pathogenic) forms that cause disease. Some different shapes of bacteria Bacteria can double in number every 20 minutes! The motility (movement) of some bacteria in culture. How fast! Pseudomonas aeruginosa Good bacteria Bacteria help to break down faeces (poo) in sewage works. Bad bacteria in the mouth cause teeth to rot. Mouth bacteria Mouth bacterium MRSA- the bacterial superbug! Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Methicillin (an antibiotic) WON’T Work to cure this infection! Bacteria Cell wall Cytoplasm Cell membrane Circle of DNA Bacteria Cell wall Cytoplasm Cell membrane Circle of DNA Sometimes has a TAIL to help it swim Structure of viruses How viruses replicate inside cells Examples of viruses A T4 bacteriophage. This infects only bacterial cells, in this case only E. coli The HIV virus. This attacks T4 lymphocytes. It is responsible for AIDS. One sneeze can transmit many cold virus particles Bird flu virus Measles virus Electron microscope picture of the measles virus Boy with measles Viruses cause warts, cold sores and verucae Conjunctivitis Foot and mouth disease is caused by a virus and is VERY infectious for cows From this To this Treatment of viral infections Virus Protein Coat Strand of DNA Virus Protein Coat Strand of DNA SMALLEST microbe Also NOT technically alive… Fungi Why did the mushroom want to go out with the toadstool? Because he was a Fungi to be with! Fungi are organisms that produce spores and come in the form of moulds, yeasts, mushrooms and toadstools. They also help things to rot and breakdown which is an essential process in the cycle of life. Examples of fungi Mould growing a bread bun There can be good forms of fungus (used to make bread/beer) and bad forms (Mould, Athletes foot and thrush). Yeast cells budding Mould and fungus causes things to breakdown Fungus taking over Athletes foot Oral thrush Thrush yeast cells Fungi Cytoplasm Cell membrane Cell wall Nucleus Starch granule Vacuole Fungi Cell wall Starch granule Vacuole Nucleus Cytoplasm Cell membrane BIGGEST microorganism Sort the cards into if they are caused by a bacteria, virus or fungus MICROBE BINGO Similarities and differences • What do bacteria and viruses have in common? • How are viruses different to bacteria and fungi? Mould • What is mould? • Why does food go mouldy? • Name 5 different methods of stopping mould growth and explain why they stop it. Mould investigation Aim: To investigate how to stop mould growing in gravy Variables Independent: Dependent: Control: Prediction • http://www.ehow.com/how_6317533_makenutrient-agar-home.html Gravy experiment results and conclusion PEER ASSESSMENT FOR AF5 Yeast • What type of microbe is yeast? • What do we use yeast to make? • What types of respiration does yeast do? Plan an investigation into one factor that affects yeast growth • You are going to put yeast, sugar, a drop of washing up liquid and warm water in a measuring cylinder • Choose one factor to change and investigate Write the Aim, prediction, and variables Aim: to observe yeast growth Time (mins) Height of bubbles (mm) The first line of defense • How can diseases be passed from one person to another? • What is the bodies’ first line of defense to stop microbes entering? Bread mould 2 week results Match the defense mechanism to its use The immune system • What is the immune system? • Which cells defend us against disease? • How do they defend us? Video Vaccination • Which cells produce antibodies? • How do these cells respond when the body is infected? • Why do vaccinations stop you getting ill again? Video