The Household Budget
advertisement
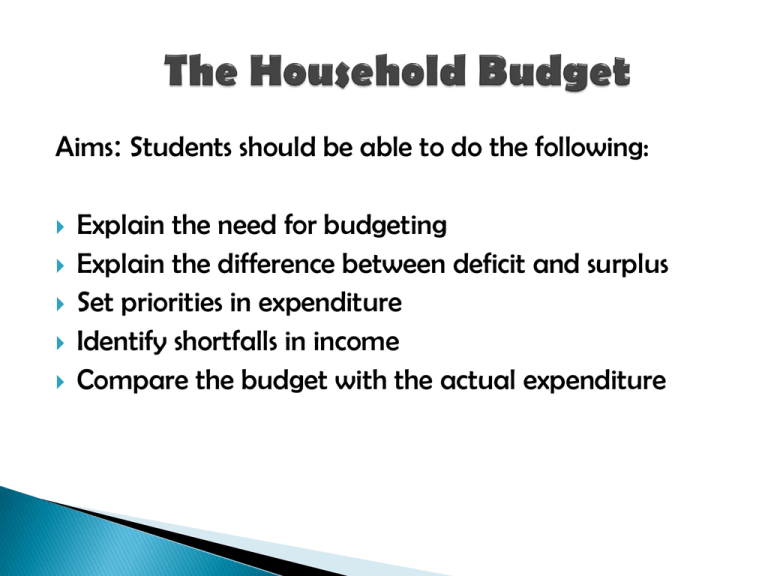
Aims: Students should be able to do the following: Explain the need for budgeting Explain the difference between deficit and surplus Set priorities in expenditure Identify shortfalls in income Compare the budget with the actual expenditure Why do households need to Budget? To make sure that they do not spend more than what they earn. What is Household Budgeting? Household budgeting is the planning of how our money will be allocated. The figures are only ESTIMATES of the actual figures involved. If we spend more than we earn, we end up with a Budget Deficit. ◦ Expenditure is Greater than Income If we spend less than we earn, we end up with a Budget Surplus. ◦ Income is Greater than Expenditure To find out if we have a Deficit or a Surplus SUBTRACT Total Expenditure from Total Income to get NET CASH. Total Income – Total Expenditure = Net Cash If Net Cash is Positive Surplus If Net Cash is Negative Deficit The Smith Family Jan Feb March Total income €2660 €2800 €2660 Total Expenditure €2700 €2200 €2600 Net Cash (€40) €600 €60 A deficit is shown in brackets ( ). In this example we can see that the Smith family had a budget deficit in January and a budget surplus in February and March. Can you give an explanation for the deficit in January? Comparing Budget to Actual figures. ◦ This is done to see where the actual are different from the budgeted. ◦ We can see where the shortfalls in income are. ◦ Allows us to be able to make whatever changes are necessary when drawing up the next budget. What to do if there is a deficit: 1. Prioritise your expenditure by Cutting back on discretionary expenditure. Find cheaper alternatives to some items. 2. Try to earn extra income. 3. Try pay bills in instalments. 4. Borrow for CAPITAL EXPENDITURE only if we can afford repayments. CAPITAL EXPENDITURE: ◦ Is spending on items that should last a long time. e.g. Washing machine, fridge, cooker. ◦ It is acceptable to borrow to pay for Capital Expenditure but not Current Expenditure CURRENT EXPENDITURE: ◦ Is spending on items necessary to run the house on a daily basis, e.g. food, clothing, petrol, entertainment. Students will now be able to do the following: Explain the need for budgeting Explain the difference between deficit and surplus Set priorities in expenditure Identify shortfalls in income Compare the budget with the actual expenditure