Employer Mentoring of Apprentices.final version 29.09.14
advertisement

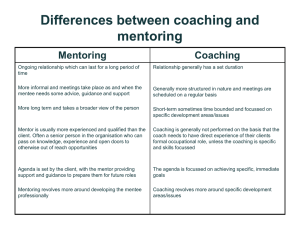
Employer Mentoring of Apprentices Name Date This was produced as part of the Apprenticeship Staff Support Programme, which was commissioned and funded by The Education and Training Foundation Administration Timing Breaks Rooms Refreshments Phones Facilities Introductions Name Background Current mentoring role? Personal objective(s) “I am probably the only person in the room who….” Agenda Apprenticeship context Role of the mentor Skills of the mentor Stages in the process Roles and responsibilities SMART targets Setting the Scene Be yourself Contribute Offer feedback … constructively Be respectful Something should be different tomorrow! Apprenticeships Provider to insert their specific Apprenticeship context What is the role of a mentor? The mentor role As a mentor, you pass on valuable skills, knowledge and insights to your mentee to help them develop personally and in their career. Definition "Mentoring is to support and encourage people to manage their own learning in order that they may maximise their potential, develop their skills, improve their performance and become the person they want to be." Eric Parsloe, The Oxford School of Coaching & Mentoring Skills of a mentor What do you think are the essential skills of a mentor? Skills of a Mentor Positivity Empathetic Motivational Confident Honest Questioning Active listening Noticing knowledgeable Caring Observing Target driven Skilled at feedback Time manager Structured Authoritative Approachable Open Stages in the mentoring process 1. Getting to know you 4. Ending 2. Goal setting 3. Progress monitoring Exercise – getting to know you Write a letter to your mentee. Include: ◦ A little about you, your background, work history and your experience ◦ What you hope to bring to mentoring ◦ What you will commit to the mentoring relationship ◦ Your hopes and expectations of mentoring Effective listening In pairs, one person talks about a hobby, holiday or passion of theirs. The other person has the role of listening. How do we ACTIVELY listen? How do we ACTIVELY listen? Maintain eye contact Encourage the speaker Check understanding / summarise Appropriate body language Exercise Draw a house Explicitness is.... ...defining, and specifying in explicit terms, what is required, so that the person has a clear mental picture of the actions, behaviour or results that are required. Draw a house Add 25 points for each window Add 100 points if you included curtains Take off 50 points for each chimney Add 75 points for a pathway Add 100 points for each tree Take off 25 points for animals Explicitness The Onion Model SMART Targets SMART targets help develop explicitness in goal setting. SMART stands for: S M A R T Specific Measurable Achievable Realistic Time-bound Creating SMART targets Work in pairs to generate 2-3 SMART targets that may be relevant to an Apprentice. Share your examples with the room and ask for feedback on ways they may be made even more SMART Exercise 2 - SMART targets How could you suggest SMARTening the following target: Apprentice X is expected to make telephone contact with 300 employers. Feedback exercise In small groups discuss how feedback is best delivered. Agree the key elements of effective feedback Prepare to feedback to the full group What is Feedback? Information about reactions to a product, a person’s performance of a task, etc. which is used as a basis for improvement. Oxford English Dictionary Considerations when providing feedback Be clear and honest Remain positive Be objective – using facts Ensure the comments are constructive Feedback should be two-way It may need to be formally followed up Discuss alternatives / advice Motivational – positive / developmental / positive Consider an appropriate environment Preparing to Give Feedback When preparing to give feedback, it can be useful to consider the conversation from three different perspectives, in order to ensure that: You are clear about the key messages you want / need to get across You have considered beforehand the possible reactions / questions of the recipient, how your feedback can be worded in a way that is least likely to provoke a difficult reaction, and how you might handle possible reactions / questions The bigger picture – the context of the conversation, what are the longer-term implications of the conversation, and what is the overall purpose of the feedback conversation Feedback exercise In groups of three allocate roles: ◦ Observer ◦ Mentor ◦ Mentee Practice providing effective feedback to the Apprentice based on their first month in your department Kolb Experiential Learning Cycle The Seven Learning Styles Visual prefer using pictures, images, and spatial understanding Aural prefer using sound and music Verbal prefer using words, both in speech and writing Physical prefer using your body, hands and sense of touch Logical prefer using logic, reasoning and systems Social prefer to learn in groups or with other people Solitary prefer to work alone and use self-study What could be barriers to mentoring success? In groups list on the left margin of a piece of flipchart the potential barriers to a successful mentoring relationship Move to the flipchart of a different group and say how you may overcome each of the barriers Case study Your apprentice suddenly starts being about 20 minutes late for work every day, having been an excellent time-keeper up to that point. Honestly - what would you do? Case study When gently persuaded, the apprentice revealed that his moped had broken and he couldn’t afford to fix it until pay-day, added to the fact that his Mum (single parent) was ill and so couldn’t drive him in. What would you do now? What support is available? Your Learning Provider Mentoring Handbook Linked-in group – ‘Apprentice Mentors’ Websites – specific support Further training Thank you! Evaluation sheets Next steps Any questions?