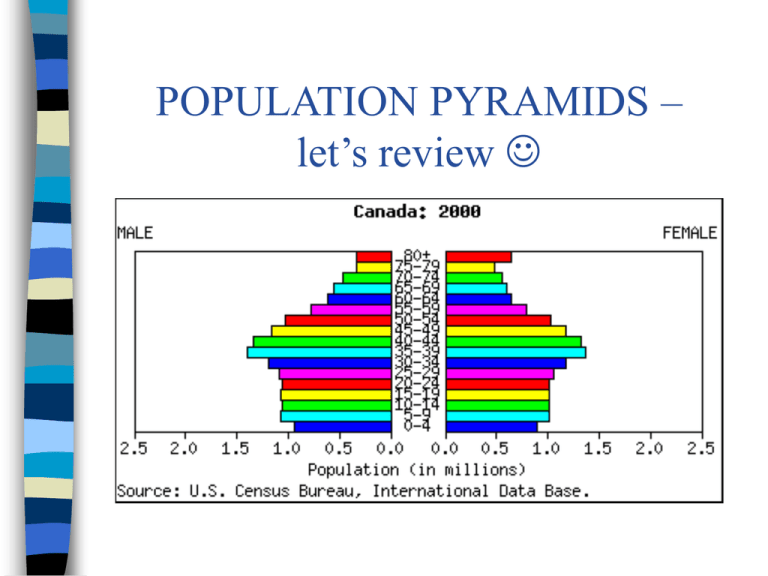
POPULATION PYRAMIDS –
let’s review
Population pyramids show the age/sex
structure of a country
Tells you what % of the population is a
certain age and gender
COHORT
A group of people of a certain age
Used to determine trends and see
similarities and differences
5 year groups are most common
DEPENDENCY LOAD
The number of people who are too old or too
young to support themselves.
They are dependent on the rest of society
Generally it includes people who are under
15 years or over 65
The higher this number is, the more taxes
have to be paid for schools, hospitals,
daycares, etc.
RAPIDLY EXPANDING
Very high birth rate
Population growing very fast (3-4% per year)
Low income countries
EXPANDING
High birth rate
Population growing (1-2% per year)
Middle to low income countries
STATIONARY
Births replace deaths
Population not changing much at all
High income countries
DECLINING
More deaths than births
Population shrinking
Potential social problems
Canada’s population
http://strategy.sauder.ubc.ca/antweiler/e
dutainment/pyramid.pdf
(2009
)
p. 23
As you look at 2009, explain the peaks
and valleys of the pyramid, starting from
1944.
Examine the following;
In partners or groups of three;
What do you see as challenges
or pros and cons for Canada in
the next 20 years based on your
observations of the two
pyramids?
Canadian Population Patterns:
Canada’s overall population density may be low,
but some parts of the country are much more
crowded than others. As a result, 2 main patterns
have developed....
1.) More than ½ of us live in large cities:
•Pattern began in the 1920’s when farm workers moved
to cities to find work in factories
•Also, a huge wave of immigrants entered Canada and
settled in cities because work was easier to find
Canadian Population Patterns:
2.) The majority of Canadians live in Southern
Canada
•The strip from Windsor, Ontario to Quebec
City, Quebec is about 1100km long, but
contains nearly ½ of the total population of the
country
•Yukon, NWT, and Nunavut have 39% of
Canada’s total land, but only about 0.3% of the
total population
How Population Changes:
•Natural Increase: is when the number of
babies born during a specific time period
is more than the number of deaths during
the same period.
•Natural Decrease: is when the deaths
exceed births during a specific time
period.
How Population Changes:
•Net Migration: to get this number
subtract emigration rate from immigration
rate
•Population Change: is found when
demographers take the natural increase
or decrease, (whichever applies) and add
it to the net migration number.
AKA: Population Growth Rate
Dependency Ratio:
Age-population ratio of those typically not in the
labor force (the dependent part) and those
typically in the labor force (the productive part).
It is normally expressed as a percentage:
(# of people 0-14 + # of people 65+)
Dependency Ratio= _______________________________
# of people aged 15-64
Dependency Ratio:
•The (total) dependency ratio can be
decomposed into the child dependency
ratio and the aged dependency ratio:
Number of people aged 0-14
Child dependency ratio=____________________________
Number of people aged 15-64
X 100
Number of people aged 65 and over
Aged dependency ratio= ___________________________
X 100
Number of people aged 15-64
LET’S DO IT !!!!
Time to calculate kiddies
According to the World Bank – these are Canada’s stats in 2011.
•
•
•
•
Total population = 34 500 000
Aged 65 and above = 4 981 800
Young, 0-14
= 5 623 500
Aged 15-64
= 23 894 700
Answers!!
Child Dependency Ratio: 23.54 per 100 working (15-64)
Old Dependency Ratio: 20.84 per 100 working (15-64)
Total Dependency Ratio: 44.38 per 100 working (15-64)
1. Make a prediction for the future dependency ratio of
Canada. What will happen to the proportion of youth,
senior and working age populations? Why?
2. What are some of the potential impacts of high
dependency ratios?
3. Suggest some possible ways of relieving the burden of
an aging population.
Dependency Ratio:
•As the ratio increases there may be an
increased burden on the productive part of the
population to maintain the upbringing and
pensions of the economically dependent.
Demographic
Trends Today
First let’s look at the
“generational groups”.
Lab task
It’s all about the boomers!!!
What has been the impact of
Baby Boomers on North
American society?
1960s
Counter-culture as
impetus for Social Change
Questioning status quo…
Music
Fashion
Drugs
Sex
Demonstrations
Peace Symbols
Political Activism
New Fashion
•miniskirts - 1964
•brightly
coloured dresses
•knee-high boots
•bell bottoms - 1964
•bikinis
Hippies
•Rejecting traditional
values and lifestyles
•Long hair
•Drugs
•Communes
Iconic moments for the Baby
boomers:
Generational
tension around
DRUGS, SEX &
ROCK N ROLL
Black Americans in the 1960s
Civil Rights Movement
Equal rights for Black
Americans ?
Laws changed, desegregation
Assassination Of ML King Jr.
sparked riots in over 100
cities.
http://www.you
tube.com/watch
?v=pi6NeuFr5
Us
Youth optimism:
John F. Kennedy
- US President from 1961-63
- Youngest elected to the office at 43
- Only Catholic President and first
Irish American president
- Assassinated on November 22,
1963
- His youth and liberal views on
social issues inspired boomers
Ask not what your country can do
Women in the 1960s
Increased enrollment in Universities
Increased women with careers.
A women’s protest movement began in the
1960s asking for equal rights for women at
home, at work and in civil court (i.e. divorce)
The Pill
-Released in 1957
Not promoted as
contraception but rather
to aid with cramps (this
reduced some opposition)
and the
•
•
•
•
Sexual Revolution
Moral Changes
Sexual Freedom
Increase in unmarried mothers
Premarital sex
Women started having
more freedom …
… Canadian
population
decreases
Woodstock- 1969
August 15-18, 1969
500,000 people
Rolling Stone called it one of
the 50 Moments That Changed
the History of Rock and Roll
War and discovery
Two others issues that dominated the USA
(& influenced Canada) during the 1960s
were the Vietnam War and Space Race.
War from 1957-1975
(US withdraws in
1973)
http://www.youtube.com/watch
?v=RMINSD7MmT4
Draft Dodgers
-20 000 – 30 000 Draft
Dodgers came to Canada
-Accepted as immigrants
Other results of the boom…
Wealth and Prosperity:
-Canada became a source of natural resources during the war, this continued
and American companies invested $12 billion between 1945-1960
-Marvin Harris developed the Cultural Materialist school of thought around
the idea that economic factors change society
Suburbia:
-Limited urban land = subdivisions outside of city limits = cars = manufacturing
jobs = Pleasantville! Malvina Reynolds - Little Boxes 1962
Education:
- Elementary and secondary schools were built in huge numbers.
- In the mid to late 60s new Universities and Community colleges had to be
built.
-Change from authoritarian education (3 R’s) to progressive education
(student driven). Also Dr. Spock’s values on parenting led to more
permissive parenting, “he ruined a generation”.
-Canada took on a tremendous amount of national debt educating the baby
boomers. But don’t worry boomers your kids and grandkids will pay the bill!
Great news!!
LAST SUMMATIVE:
Your Generation – Song
analysis – The Why of ‘Y’
Discuss;
How are baby boomers
continuing to affect
society today?
In partners or groups of three:
• Brainstorm what you imagine your future will look like.
•When will your career start?
•How many careers do you imagine you’ll have?
•When will retirement start for you?
•What will it look like? What activities will you be
doing?
Video Clip- Sherry Cooper “The New Retirement”
How the Baby Boomers continue to
affect change via their choices and
their children’s choices.
The impact of the Echo Generation
and Gen Y.
Watch Doc Zone x2
• “Boomerang Generation”
• “How we got Gay”