Behaviorist and Humanist Theories
advertisement

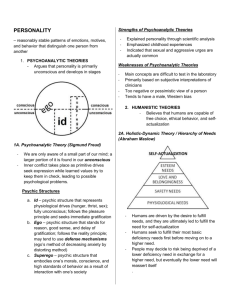
BEHAVIORIST AND HUMANIST THEORIES Unit 5 Lesson 4 OBJECTIVES Review additional psychoanalytic theories. Indentify contributions of Thorndike, Skinner, Maslow and Rogers to study of personality. Compare and contrast behaviorist and humanist theories of personality development. WARM UP If Freud said that pleasure drives personality formation, what did the others say drives it? Jung – Collective unconscious (archetypes) Adler – Inferiority Erikson – Socialization Horney - Security ERIKSON’S PSYCHOSOCIAL DEVELOPMENT 65+ Wisdom 40-65 Care 18-40 Love 12-18 Fidelity 5-12 Competency 3-5 Purpose 1.5-3 Will B-1.5 Hope LOCUS OF CONTROL SCALE BEHAVIORIST / SOCIAL-COGNITIVE MODELS BF Skinner Response Tendencies - personality shaped via learning Albert Bandura Social Learning Theory Observational Learning Self-Efficacy - expectation of success Julian Rotter Locus of Control – perception about causes of events in life Internal LOC –personal decisions & efforts External LOC –fate, luck, other external circumstances HUMANISTIC THEORIES Alternative to negative, focus on positive Born with positive drive to grow & improve (innerdirectedness). HUMANISTIC THEORIES Abraham Maslow Hierarchy of Needs – humans strive to realize full potential once they have satisfied basic needs. HUMANISTIC THEORIES Carl Rogers Self-concept: all thoughts, feelings, and beliefs about ourselves Real vs Ideal Self Incongruence – discrepancy Congruence – match = fully functioning person Unconditional Positive Regard - total acceptance & love from others no matter what Conditions of worth – requirements for earning UPR from others THINK-PAIR-SHARE In your notes, won’t be collected so be honest! Who is your most significant other at this time? Do you have UPR for this person? Explain. Does this person have UPR for you? Explain. Are there conditions of worth in your relationship? If so, what are they? A SURVEY… Give yourself one point for each of the following A responses: 1, 2, 4, 6, 9, 12, 13 Give yourself one point for each of the following B responses: 3, 5, 7, 8, 11, 14, 15 If your A score is higher than 5, you agree more with the behaviorist view of personality. If you B score is higher than 5, you agree more with the humanist view. Statement 10 can be interpreted as either view. CLOSURE How do psychoanalytic, humanistic, and behavioral perspectives of personality differ? Psychoanalysts emphasize unconscious forces in dvpt of personality Humanists emphasize rationality and natural desire to be all we can be Behavioral (or social-cognitive) theories emphasize impact of learning and cognition on dvpt. HOMEWORK Write down three traits or characteristics that best describe you. Find three other people and ask them what 3 words they would use to describe you.