Analyzing Literature
advertisement

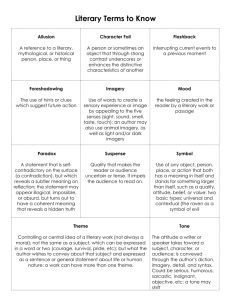
Analyzing Literature Guide for Students Literary Analysis = Argument O Make a claim about the work, then support it O Purpose: persuade readers your analysis + interpretation is reasonable/logical O NOT your opinion about the work, but your interpretation + analysis Why Literature? O Way to experience a way of life, time period, culture, emotion, deed, event, etc… O Skills you bring to the table: close reading, breakdown of structure, word choice of author, character motivations, patterns of language, literary devices Process of Analysis O Multiple readings O Specific word choices O Setting + culture O How the writer: uses words to create meaning, how characters speak (dialect/jargon), who is telling story, etc… O ANNOTATE Literary Terms O Character: flat/round O Drama: plays O Fiction: imaginative prose O Foreshadowing: prepare the reader by introducing clues O Narrator: who tells story (POV) O Personification: giving animals/inanimate objects human characteristics Literary Terms O Plot: Action/storyline O Setting: where and when O Symbolism: use of a thing or person or event to create familiar emotion and/or intellectual response in reader So – To Summarize 1. Read through for enjoyment first, then reread 2. Note diction (how writer uses words to convey meaning), setting, culture, POV, imagery, anything writer does that stands out to you. 3. ANNOTATE your findings as you read. Mark text/take notes Yours Mary Robison O Diction: - “Allison struggled away…limping” (7) - 43 yrs. Difference in age - Gift check from nasty relatives signed “Jesus H. Christ” – “vigil candles” - Seem happy together – language is common, everyday language - “Allison began to die” (9) O Setting/Culture: - 1983 – set in modern time in suburban setting, fall - American culture – daycare, doctor, Halloween - judgmental culture about age differences in marriage O POV: - third person limited (see many things only from outside, but then get Clark’s POV there at the end. – sudden and powerful – the pain of loss O Imagery: - White Renault (?) - fall imagery “twig and leaf-littered porch” “thick blond hood” “bright-dyed denims” - pain + death imagery “Struggled…limping” “gutted and carved” “ferocious and jagged” “began to die” “pulse cords fluttering” “awful, plaguing thing” Choices in Analysis O Question: For me to write an analysis about this story, I have to identify what elements create important meaning and then how the writer creates it. O Because I find the age difference fascinating since the woman dies first, I will want to focus on that… Other Analysis Choices O How the various literary elements work together in a specific work to produce meaning O How two different literary works treat the same subject or literary element(s) O How ideas and/or elements in literary works relate to larger ideas relating to political, religious, societal, economic, or aesthetic conditions Support O Text evidence: - secondary sources - direct text - paraphrase or summary O Other critics’opinions O Social +/or historical context O Do not overuse a single source What to Do in an Analysis O Focus on a single attribute or aspect of a literary work(s) O Make sure your thesis is arguable O Make sure you defend your thesis with specific text evidence Examples O Bad – Really Bad: Atlas Shrugged is a great novel about good vs. evil. O Better – but not by much: Atlas Shrugged, a novel, personifies good vs. evil. O Best: Atlas Shrugged, a novel personifying the author’s view of good and evil develops into a philosophical argument for capitalism through direct characterization.