Kenai Evaluation Presentation (Danielson) PPT
advertisement

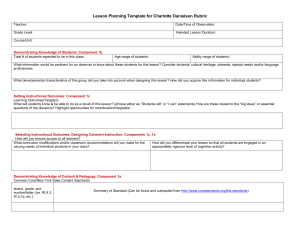
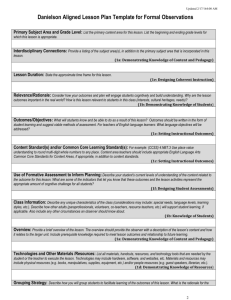
The Role of Teacher Evaluation in Becoming a Highly Reliable School District The Kenai Peninsula Borough School District Presentation to ASDN Spring Leadership Retreat April 10, 2013 KPBSD’s Teacher Evaluation Journey • Background-why did we make the change? Dr. Steve Atwater, Superintendent • How we made the change Sean Dusek, Assistant Superintendent for Instruction • Implementing the change Melissa Linton, Principal Kalifornsky Beach Elementary • Making it all work Tim Peterson, Director of Human Resources Putting your new evaluation system in place, how do you feel? Four Keys To A Highly Reliable School District • Sustaining a commitment to a dual bottom line • Centralized procedural control and standardization • Flexibility with situational improvisation • Combining opposite operating modes Teacher Evaluation, One Piece of the Effective Instruction Puzzle Professional Development Teacher Evaluation Collaboration Curriculum with Embedded assessments The Teacher Evaluation Piece Provides Focus • Evaluation process helping to drive intentional instruction • Commitment to training our principals – inter rater reliability • Unrelenting focus on 3c • Evaluation process focuses our collaborative work • Evaluation process driving professional development and providing feedback on our curriculum/assessment Getting Started • KPEA and KPBSD – a partnership • Committee work – 4 teachers including KPEA president – 3 principals – 2 District Office • Information – Semi-annual surveys – Administrator feedback – Site Councils – Board work sessions • Upcoming changes – More Board and community involvement KPBSD Standard Model Evaluation Process 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Pre- Conference Training Self-Reflection Conference Classroom Walk-Throughs Informal Observations Pre - Observation Conference Formal Observation Post observation Conference Evaluation Summary Conference Getting closer • Calibration – Dedicated time at all administrator meetings • Video • Real evaluations – evidence – – – – – Utilize quality processes Vocabulary Focus on engagement Decide what should be in narrative Next steps • Use our own teachers in videos • Peer walkthroughs – structured • Electronic observation gathering Refinement • Danielson model – – – – Fitting our needs and priorities Condensing components and elements Different for tenured and non-tenured What makes sense for us…. • Student Learning – Moving to 2 Domains – Instruction and Learning/Growth Structure of Refinement • Instruction – – – – – – Culture of Learning Planning and Preparation Classroom Environment Engagement Reflection Professional responsibilities • Student Learning and Growth – – – – Standardized assessment results Common assessment results Portfolios Student Learning Objectives Domain 1 Planning and Preparation Domain 2 Classroom Environment 1a 1b 1c 1d 1e 1f 2a 2b 2c 2d 2e Demonstrating Knowledge of Content & Pedagogy Demonstrating Knowledge of Students Setting Instructional Outcomes Demonstrating Knowledge of Resources Designing Coherent Instruction Designing Student Assessment Creating an Environment of Respect & Rapport Creating a Culture of Learning Managing Classroom Procedures Managing Student Behavior Managing Physical Space The Danielson Framework for Teaching Domain 4 Professional Responsibilities Domain 3 Instruction 4a 4b 4c 4d 4e 4f 3a 3b 3c 3d 3e Reflecting on Teaching Maintaining Accurate Records Communicating with Families Participating in a Professional Community Growing and Developing Professionally Showing Professionalism Communicating with Students Using Questioning and Discussion Techniques Engaging Students in Learning Using Assessment in Instruction Demonstrating Flexibility & Responsiveness Instructional implications of the CCSS were added in the 2013 edition of FfT Domain 1 Planning and Preparation Domain 2 Classroom Environment 1a 1b 1c 1d 1e 1f 2a 2b 2c 2d 2e Demonstrating Knowledge of Content & Pedagogy Demonstrating Knowledge of Students Setting Instructional Outcomes Demonstrating Knowledge of Resources Designing Coherent Instruction Designing Student Assessment Creating an Environment of Respect & Rapport Creating a Culture Culture of of Learning Learning Managing Classroom Procedures Managing Student Behavior Managing Physical Space Domain 4 Professional Responsibilities Domain 3 Instruction 4a 4b 4c 4d 4e 4f 3a 3b 3c 3d 3e Reflecting on Teaching Maintaining Accurate Records Communicating with Families Participating in a Professional Community Growing and Developing Professionally Showing Professionalism Communicating with Communicating withStudents Students Using Questioning Questioning and and Discussion DiscussionTechniques Techniques Engaging Students Students in in Learning Learning Using Assessment Assessment in in Instruction Instruction Demonstrating Flexibility & Responsiveness The Framework for Teaching Evaluation Tool • • • - 4 Domains 22 Components 76 Elements Rubric descriptions for each level of performance (LoP) - Critical attributes that for each (LoP) - Possible examples for each (LoP) Danielson in the current climate • Framework Evaluation Instrument, 2013 edition • Major instructional implications and themes of Common Core State Standards Process • Need • KPEA - Buy in • Teacher and administrator training • Modules, key leaders at the schools • http://www.kpbsd.k12.ak.us/departments.aspx?id=19400 • Committee • Planning • On Going • Leaders – become co-facilitators and presenters • Meetings • Board of Education Implementation • Teacher Evaluation for Continuous Growth – Two distinct tools – Kenai Model (Framework) • Five year phase in • Continue to change – Teacher Enrichment Model Challenges • Time – Accountability – Mandated Observations (Committee) – Mandated Meetings (Committee) • Culture Shift – Continuous Growth Model – Added step (Committee) – Same old stuff • Technology - Resources – Lack of electronic support • State Mandates – Shifting target Teacher Evaluation- One Piece of the Effective Instruction Puzzle BEFORE NOW Questions or Comments