1181aa6c-6172-4b75-a627
advertisement

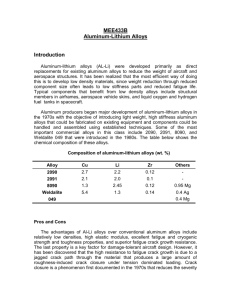
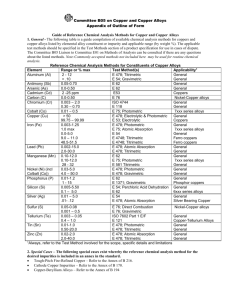
Alloys أحمد عبد العزيز الحسين أخصائي تركيبات سنيه في وزارة الصحة األردنية محاضر غير متفرغ في جامعة العلوم والتكنولوجيا األردنية Ahmad Abdul Aziz Alhussien Prosthodontist at M.O.H Part time lecturer at J.U.S.T BSc , MSc, Jor. Board/ prosthodontics Introduction • Alloy: a mixture of two or more metals • Pure metals are rarely used in dentistry because they are weaker than they are when mixed with other metals. • Cast metal alloys can be used for bridges, partial or complete denture bases Classification of dental casting alloy (ADA) • High noble alloys “precious metals” – at least 60% noble. 40% of which is gold. The remaining 40% is base metal • Noble alloys(semiprecious) – at least 25% noble (no gold requirements). 75% base metal • Base metal alloys – Less than 25% noble • What does noble mean? – Does not corrode readily • Noble metals are: Au, Pd, Pt Noble Alloys • Gold alloys – Most corrosion resistant – Pure gold is 24 karat, 100% – Properties: • Low Hardness (resistance to penetration) • High Malleability (ability to be shaped by tapping) • High Ductility (ability to be elongated) Noble alloys • Platinum is not used much because: – Too expensive – High melting point – Difficult to mix with gold • Palladium is used more widely because: – Good corrosion resistance – Increases hardness of alloy • Silver is precious but not noble because it corrodes. Base metal alloys • < 25% noble metal • Primary base metals (non-precious): – Copper .. Added to to increase hardness – Silver .. Added to increase hardness – Nickel .. Biocompatibility issues – Tin .. Added to increase flowness – Zinc .. added to decrease oxidation • Stiffer than gold alloys, higher stress resistance Base metal alloys • Drawbacks: – Difficult to finish and cut – More equipment to manufacture – Higher casting temperature – Biocompatibility issues Base metal alloys • Small crystals produce better qualities than larger ones “malleability and ductility” • Some alloys such as gold maybe reheated (annealing) to improve properties “hardness” • Reheating base metal alloys is not recommended “corrosion” Biocompatibility • Nickel is associated with allergy (9-12% of population), especially in women – Seen on free gingival tissue in contact with metal – Mostly more sever with fixed prosthesis – Skin response may occur • Beryllium, added to Ni-Cr to reduce fusion temperature and create smaller crystals: – Can also cause allergy. – Inhalation can cause lung disease called berylliosis Base metal alloys • stainless steel alloy (18/8) – (18% chromium, 8% nickel) Concepts • Solder Alloys that are used to join metals together or repair cast restorations • Welding : Process of fusing two or more metal parts through the application of heat, pressure, or both, to produce a localized union across an interface between the parts. Implant materials • Used as anchors for prosthetic replacement of missing teeth • Three main types: – Subperiosteal – Transosteal – Endosseous Implant materials • These implants are made of titanium or titanium alloy, used for its biocompatibility: • Pure titanium is not as rigid as the alloy • These implants are retained by intimate contact with bone (osseointegration) • Some implants are coated with Calcium phosphate (hydroxyapatite) or plasma proteins to improve osseointegration