File
advertisement

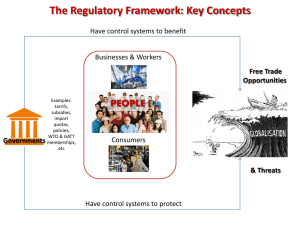
Protectionism A2 Economics Unit 4 Aims and Objectives Aim: • Understand protectionism Objectives: • Define protectionism • Explain methods of protectionism • Analyse the effects of protectionism • Evaluate the usefulness of protectionism Starter • There is no guarantee that gains of trade are equally distributed, and although restrictions on trade will probably reduce world welfare, individual countries may feel it is in their interest to do so…… • Economist Article 2011 Definition Protectionism: Government actions and policies that restrict or restrain international trade, often done with the intent of protecting local businesses and jobs from foreign competition. restrict or restrain international trade, often done with the intent of protecting local businesses and jobs from foreign competition. Starter • In groups decide on as many methods of protectionism as you can. •Tariffs •Subsidies •Quotas •Embargoes •Voluntary Export Restraints Techniques of Protectionism Tariffs • Specific – tax at a fixed rate per unit. • Ad-Valorem – a tax which is a % of the price of the unit. • Taxes on imported goods. • Size of tariff depends on PED. Price Techniques of Protectionism Tariffs Domestic Supply H Price With Tariff F P+T G P J World Price K L Domestic Demand B E A C Qty Techniques of Protectionism Tariffs • World Price before tariff is 0P • Before tariff domestic demand was 0C and domestic suppliers were producing 0B. • Imports were BC Techniques of Protectionism Tariffs • • • • Tariff imposed price rises to P+T Domestic demand falls to 0A Domestic output rises to 0E Imports are now EA Techniques of Protectionism Tariffs • Domestic suppliers have gained P,P+T, H, J at the expense of consumers. • HFKL = revenue from tariff • Overall net loss is triangles – JHL & FKG – the tariff has reduced welfare as a whole. Techniques of Protectionism Embargoes • Prohibition of trade with a country to put pressure on its government to change policies. • Leads to smuggling and black markets • http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-latinamerica-16951854 Price Techniques of Protectionism Subsidies Consumer Surplus S • Before Subsidy • Government then subsidises to shift the supply curve downwards. Producer Surplus Qty Price Techniques of Protectionism Subsidies Consumer Surplus S • After Subsidy S1 • Supply curve shifts down, consumer and producer surplus increases. Producer Surplus Qty Techniques of Protectionism Quota • Limit on the number of imports allowed into a country. • Used to benefit producers but not consumers. Techniques of Protectionism – Voluntary Export Restraints (VER) • One government persuades another to pressurise its exporters into limiting supplies into markets. • EU had one with Japanese car makers which reduced competition and lead to high consumer prices. Is Protectionism a good thing? • http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/programmes/hard talk/9366475.stm • Create a spider diagram of the arguments for and against protectionism in preparation for a debate/argument.