Formation of the Universe Test Review Packet
advertisement

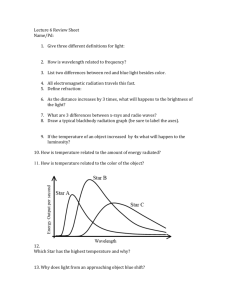
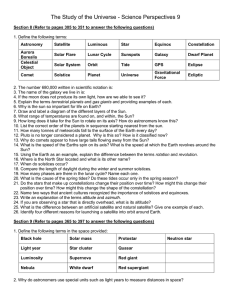
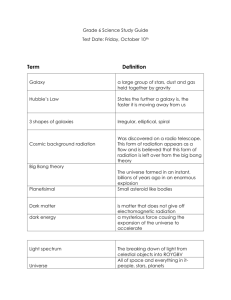
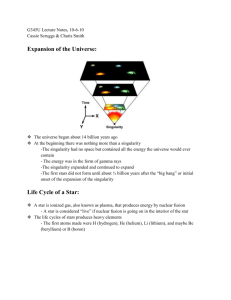
Unit LEQ: What is Science and how does it help scientists investigate the Universe? A Section 1: What is Science? Vocabulary: 1.Hypothesis 2.Inference 3.Observation 4.Theory 5.Law 6.Independent variable 7.Dependent variable 8.Quantitative observations 9.Qualitative observations Concepts: 10. What are the steps of the Scientific method in order? 11. Once you’ve reached your conclusion and you’ve accepted your hypothesis, what needs to happen to have it accepted as a theory? 12. Explain the difference between a Theory and a Law. 13. Which one is more likely to change in the future, Theory or Law? Explain why. 14. In the hypothesis “If we increase the amount of salt in our salt solution by 10g, then the size of the crystals formed will increase” identify the Independent and Dependent variables. IV: DV: 15. In the hypothesis above, which variable is QUANTIFIED? 16. The scientist made some observations of her crystals formed. She stated that her largest crystal was 10mm in diameter and that the water was cloudy. Which observation is QUALITATIVE? B Section 2: What is the chemical composition of Stars? Vocabulary 1.Atom 2.Element 3.Proton 4.Neutron 5.Electron 6.Atomic number 7.Mass number 8.Isotope 9.Nuclear Fusion Concepts 10. Draw a picture showing the parts of an atom. Mark the charges of each subatomic particle. 11. Complete the chart below. Element Atomic Number Mass Number (Atomic Weight) Sodium 11 23 Chlorine 17 Neutrons 11 6 Carbon 6 14 Hydrogen 1 1 Hydrogen (deuterium) 2 1 Electrons 18 Carbon Hydrogen (tritium) Protons 6 1 3 12. Using the chart above, what makes Carbon (mass number 14) an isotope of Carbon (mass number 12)? Explain. 13. What two elements make up the majority of the composition of a star? C Section 3: What evidence exists regarding the formation of the universe? Vocabulary: 1.Electromagnetic Spectrum 2.Doppler Shift 3.Spectroscope 4.Red Shift 5.Background Radiation 6.Hubble's Law 7.Big Bang Theory 8.Light Year Concepts: 9.Use the diagram of the electromagnetic spectrum to answer to following questions: a. What wavelength range does human eye see between? b. Which part of the spectrum has longest wavelength? 10. The electromagnetic spectrum is radiation, what is radiation? 11. Describe Earth’s motions & what effect it has on Earth. 12. How do astronomers determine the elements present in a star? 13. How do astronomers know the universe is expanding? 14. State Hubble’s Law 15. More distant galaxies have greater red shifts. What does this indicate about the universe? 16. How old do astronomers believe the universe to be? D Section 4: What evidence exists regarding the formation of the Solar System and Earth? Vocabulary 1. Solar Nebular Theory 2. Nebula 3. Supernova 4. Pulsar 5. Main-Sequence 6. Gravity 7. Red Giant 8. Super Giant 9. White Dwarf 10. Black Hole 11. Geocentric 12. Heliocentric Concept 13. Compare and Contrast how a HIGH Mass, LOW Mass, and a AVERAGE Mass (Sun-like) star evolves through its life cycle. 14. Label the H-R diagram Absolute magnitude Temperature Supergiants Main Sequence Stars Red Giants White Dwarfs Red Dwarfs Blue Giants Sun Place a where a very bright, but cool star would be Place a at the next stage our sun will evolve to Place a where a star is about Earth size, yet very hot Place a + where a star is fusing Hydrogen into Helium