New England Colonies: Pilgrims, Puritans & Economy
advertisement
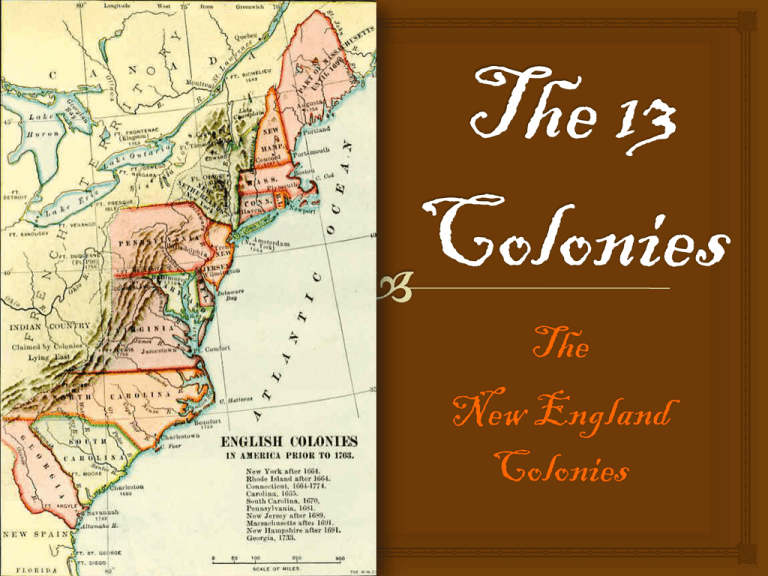
The New England Colonies 5.4 Students understand the political, religious, social, and economic institutions that evolved in the colonial era Settling New England • Pilgrims (people who make journeys for religious reasons) wanted to move to the North America to have religious freedom and to make money. • Pilgrims left England on the ship called the Mayflower in 1620 with a charter from the king which gave them approval to settle in North America • The Mayflower headed toward North America and landed in Massachusetts, thus starting the Plymouth colony. • Mayflower Compact – a compact signed on the Mayflower that created a new idea of self-government and majority rule. • Plymouth colonists farmed, fished, and traded furs. • William Bradford was the leader of the Pilgrims. • Puritans wanted to leave the Church of England (wanted to make it PURE). http://www.historyplace.com/united states/revolution/mayflower.htm • John Winthrop led/governed the second group of Puritans to settle in the Massachusetts Bay Colony. They named their settlement Boston. • Most early settlements in the Americas were built along the Atlantic coast which made it easier for the colonists to get supplies from the English trading ships. • The settlers of Boston did not welcome people with different beliefs from their own because they believed that dissent (disagreement) might hurt their colony. • Roger Williams disagreed with the Puritans – Believed that the church should be separate from the government – Felt that people should not be punished for having different beliefs • In 1636, Williams bought land from the Native Americans and called it Providence (in modern day Rhode Island). This settlement allowed freedom of religion. • Settlers who wanted more economic opportunities moved to the area of New Hampshire. • Settlers left the poor soil of Massachusetts and moved to the Connecticut River Valley. • In the Connecticut River Valley, Metacomet (also known as King Philip), the leader of the Wampanoag Indians, started the King Philip’s War which resulted in English rule over tribal lands. Life in New England • Religion affected how the Puritans lived, worked, and spent their free time. EVERYONE was required to attend church. • Schooling was required in the New England colonies for one main reason– to learn how to read the Bible • The first English colonial college, Harvard University, was founded to train ministers • New England Colonies had more schools than any other English colony. • At the center of each town there was a common , a park-like area shared by all townspeople where they kept the livestock such as cattle, hogs, and sheep for food, leather, and wool. People built their homes around the common. • Each town had a meeting hall were where the town meetings were held where male church members could have a voice in how the colony was governed. Inside view of the Old South Meeting House in Boston Home Life Women and Girls: • Prepared/ preserved (stored) food • made every day items (soap, brushes, candles, etc.) • made clothing • took care of the children (most families had 7 or more children) Men and Boys: • Hunted for food, furs, and hides • cut the firewood • made their own tools • patrolled the edges of the towns • worked in the fields (mainly corn, pumpkins, squash, etc.) New England’s Economy • Farmers sold or traded their surplus goods for other goods. • Farming led the way to a free-market economic system, meaning the farmers sold their goods to merchants who shipped them to England to sell them for more than the merchants had paid. • Colonist used the forests in New England to build houses, barns, churches, fences, and ships and sold surplus lumber to Europe and other colonies. • Fishers caught fish such as cod, herring, and mackerel. Trading became the center of the region’s economy • The English rule insisted that the colonies send their exports (goods being sent from the country) only to England or English colonies. • The King also expected the colonists to buy only English-made imports (goods brought into a country) • Triangular Trade Routes connected England, English colonies, and Africa, and carried goods from all three areas to trade among each another. • The Middle Passage was the long trip across the Atlantic Ocean that carried enslaved Africans from Africa to the West Indies. S.P.E.C. Social Political Economic Cultural Relationships/ Religion Governments/ Laws/ Leadership Money/ Financial Arts/ Education/ Food Pilgrims-traveled as Mayflower a group for religious Compact reasons William Bradford Religious freedom (Mayflower) Free-market economic system Schooling to read the Bible Lumber, fish, crops, furs Women preserved food Puritans-wanted to break free from Church of England and to refine, or make pure, the beliefs Import/ export Most items were handmade (clothes, soap, candles, tools, etc.) John Winthrop (Boston) Roger Williams (Rhode Island) Triangular trade route Write a Letter! W2.4 Write persuasive letters or compositions • Use the facts on the SPEC page you have completed and draft a one page persuasive letter. • You live in the New England colonies in the 1600’s and you want your cousin from England to come visit you. What facts and details would you include in your letter to persuade him or her to come?