Muscles of the Upper Limb
advertisement
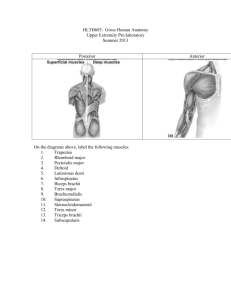
Muscles of the Upper Limb Muscles equal movement… What muscles do you already know? Questions What are the three types of muscle contractions in the body? How can you remember which muscles move a specific joint? What happens to the muscles at a specific joint during each type of muscle contraction? Hint: choose a joint, then figure out the muscles that move it and the movements it makes. Then, apply this knowledge to each type of muscle contraction. Posterior View of Back Levator Scapulae Rhomboid Minor Supraspinatus Infraspinatus Teres Minor Latissimus dorsi Rhomboid Major Motions of Muscles Trapezius Scapular elevation, adduction, retraction, upward rotation and depression, also extends neck Latissimus Dorsi Adductor, extensor & internal rotator of arm Rhomboids Assist trapezius in downward rotation of the scapula and adduction or retraction of scapula Levator Scapulae Elevates the scapula and helps rotate the scapula downward Muscles of the Rotator Cuff Supraspinatus Teres minor Infraspinatus Subscapularis - Sits on anterior side of Scapula Motions of Muscles for Rotator Cuff Supraspinatus Abducts the shoulder Infraspinatus Laterally Rotates the Shoulder All three of these muscles help stabilize the shoulder joint Teres Minor Laterally rotate the shoulder Subscapularis Rotates humerus medially, stabilizes the shoulder Muscles that Move the Humerus Pectoralis Major Deltoid (anterior and lateral heads) Coracobrachialis Motions of Muscles Deltoid Anterior Head Flexes and medially rotates the shoulder joint Lateral Head Abducts the arm Posterior Head Extends and laterally rotates the arm Coracobrachialis Acts as a flexor and adductor of the arm Teres Major Medial rotator, adductor and helps extends the humerus at the arm Pectoralis Major Internal rotation, adduction and flexion of the arm Muscles that Move the Humerus – cont’d Coracobrachialis Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior Motions of Muscles Pectoralis Minor Elevates the ribs and depresses and protracts the scapula Serratus Anterior Upward rotation, abduction or protraction of the scapula Elbow Flexors / Extensors – Anterior Biceps brachii Pronator teres Brachialis Brachioradialis Motions of Muscles Biceps Brachii Supinator in the forearm, acts to flex the elbow Brachialis Acts as an elbow flexor Brachioradialis Elbow flexor Elbow Flexors / Extensors – Posterior Triceps brachii (short head) Triceps brachii (long head) . Motions of Muscles Triceps Brachii Main extensor of the forearm Has three heads Short, long and medial Muscles of the Forearm – Anterior Biceps brachii Brachioradialis Muscles of the Forearm – Posterior Brachioradialis Triceps brachii (lateral head) Extrinsic Hand Muscles – Anterior Flexor carpi radialis Palmaris longus Flexor carpi ulnaris Flexor digitorum superficialis Extrinsic Hand Muscles – Posterior Extensor carpi radialis longus Extensor digitorum Extensor carpi ulnaris Extensor carpi radialis brevis Extensor digitorum minimis Motions of Muscles Using the wrist as an example, deduce the muscles that are responsible for the movements that happen around that joint. What are the movements around the wrist? Flexors Flexes hand and wrist Adducts and abducts wrist Extensors Extends hand and wrist Adducts and abducts wrist Muscle Contractions What are the 3 types of muscle contractions? Concentric (___________) Ex. Bicep shortens when lifting an object Eccentric (____________) Ex. Bicep lengthens when putting same object down Isometric (________) When trying to lift an immovable object! Back to the Questions: What are the three types of muscle contractions in the body? How can you remember which muscles move a specific joint? What happens to the muscles at a specific joint during each type of muscle contraction? Antagonist vs. Agonist Muscles How do muscles work together in the human body? One muscles (extensor) is required to move the bone in the opposite direction and stretches opposite the muscle (flexor) The flexor and extensor in this case are described as anatagonistic muscles Antagonist vs. Agonist Muscles Agonist Muscle The muscle primarily responsible for movement of a body part Antagonist Muscle Muscle that contracts the agonist, lengthening when the agonist muscle contracts Antagonistic Pairs What are some example of Antagonist and Agonist muscles in the upper limb? Biceps Brachii and Triceps Brachii When you Flex your Biceps, your triceps extends Deltoid and Latissimus Dorsi When you abduct your shoulder your deltoid flexes and your latissimus dorsi extends