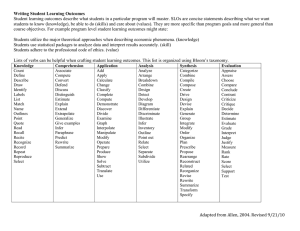
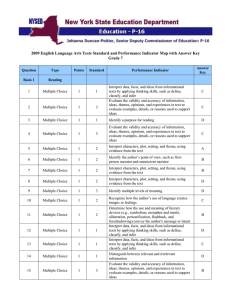
Example - Garnet Valley School District
advertisement
Cross-Curricular Vocabulary So you will know what a question is actually asking you to do… ANALYZE • To break something down into its component parts and then show how the parts are related to each other. - Example: Analyze the map below. - Example: Analyze how the human body works. BIAS • To influence in a particular direction. - Example: Can you recognize any bias in this portrait of Pocahontas? - Example: Explain how the author used bias in this piece of writing. CATEGORIZE • To organize into groups based on similarities. - Example: Categorize the following compounds based on their properties. CAUSE • The producer of an effect, result or consequence. - Example: List the causes of the American Revolution. - Example: Discuss the cause and effect relationship shown in the story. CITE • To quote or refer to as proof or example. - Example: Describe the conflict that arises between the brothers. Cite two examples from the story to support your answer. CLASSIFY • To arrange or organize based on similarities. - Example: Classify the following as either a mixture or a compound. CONCLUDE • To reach a decision or form an opinion about. - Example: Conclude-was your hypothesis supported by the evidence? - Example: Based on the evidence collected, what can you conclude about opposing forces? COMPARE • Shows how to or more things are both similar AND different. -Example: Compare The Outsiders novel to the movie version. - Example: Compare the forms of government found in the United States and in China. DESCRIBE • Write about the most important parts of the topic. Be specific about characteristics, properties and qualities of the topic. - Example: Describe the setting of To Kill a Mockingbird. - Example: Describe what it was like to live during the Colonial Times. DETERMINE • To find out or come to a decision about based on calculation, investigation, or reasoning. - Example: Using the data in the table, determine if Bubba’s conclusion is correct. EFFECT • Something that is produced by a cause. • The power to produce an outcome (influence). Example: What was the effect of Paul Revere’s ride? ESTIMATE • To calculate an approximate value or amount. - Example: If Milly is going to purchase a DVD for $25.79, a pair of socks for $4.23 and a picture frame for $13.88, estimate how much money she will give the cashier. EVALUATE • Tells you to present both the positive and negative aspects of something. - Example: Evaluate the impact of the discovery of fingerprinting. • To find the numerical value of - Example: Evaluate the following expression. EVIDENCE • A thing or things that help form or support a judgment or conclusion. - Example: What evidence did Sydney find to support her conclusion. - Example: Support your conclusion/thesis with evidence. EXPLAIN • Write about a topic so it is easily understood. Give the “how” and the “why” of events or situations. - Example: Explain the main conflict in the passage and how it was resolved. - Example: Explain the steps you took to solve the equation. GENERATE • To produce or create. - Example: Generate a scatter plot of the 2 sets of data. IDENTIFY • Pick out or find the most important ideas about a topic. - Example: Identify who the Pilgrims were and why they came to America. - Example: Identify the protagonist and antagonist of the story. INDICATE • To state or express briefly. - Example: Indicate whether or not you agree with the terms set forth in the Treaty of Paris. INFER • To come to a conclusion based on evidence or clues. - Example: Read the dialogue between these two characters. What can you infer about their relationship? - Example: Dory walks into the house wet and carrying an umbrella. What can you infer the weather is like outside? INTERPRET • Translate, solve, or comment on a subject and give your judgment or reaction to the problem. - Example: Interpret the message conveyed in this painting by John White. - Example: Interpret the data contained in the graph. OPINION • A personal view or attitude. - Example: Provide your opinion on wearing school uniforms at the middle school. PREDICT • To tell what will happen based on experience and/or evidence. - Example: Based on what you know about the monkey’s paw, predict what will happen when Mr. White wishes Herbert alive again. PROJECT • To calculate, estimate or predict based on present data or trends. – Example: Project the next number in the following pattern. RELATIONSHIP • Emphasize connections and associations in a descriptive form. - Example: What was the relationship among the British colonies? - Example: Identify the relationship between the number of coils and the strength of the electromagnet. SIMPLIFY • To reduce or make easier to understand. - Example: Simplify the variable expression. SUMMARIZE • Provide a shortened version of the main points. Do not include details. - Example: Summarize the plot of The TellTale Heart. - Example: In your own words, summarize the powers of the Supreme Court. SUPPORT • To argue in favor of something. • To provide additional evidence or information. - Example: Support or refute the following idea. THESIS • A statement or proposition that is maintained by factual argument - Example: Develop a thesis statement on whether or not Andrew Jackson was a good president. Support your statement with evidence. TRACE • Present the order in which something happened. - Example: Trace the events that preceded the Boston Tea Party. TREND • The general direction in which something moves. – Example: Draw in the trend line in this scatter plot. WITH HELP FROM: • • • • • • • www.thefreedictionary.com www.merriam-webster.com www.howtostudy.com www.educationatlas.com www.studygs.net www.googleimages.com Various GV teachers!